Fig. 3.
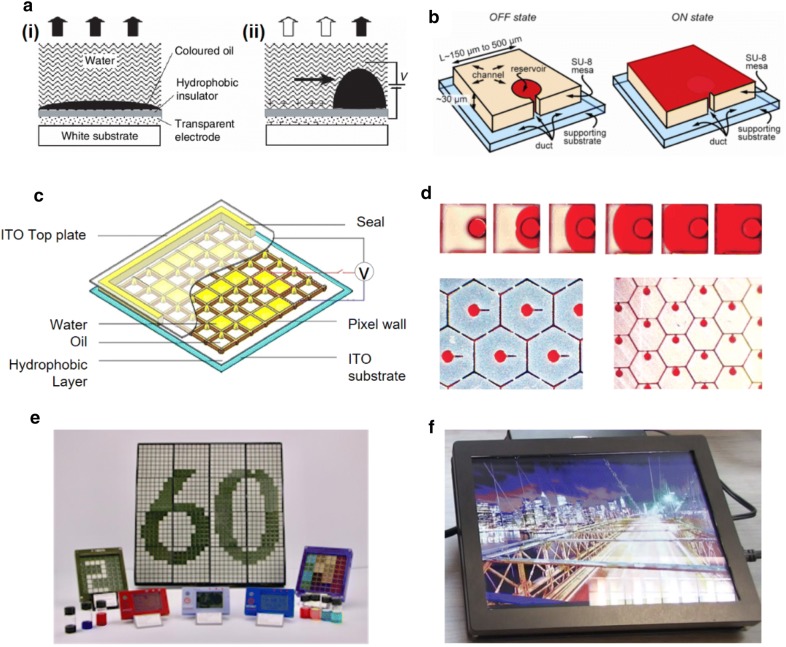
Technologies for electrowetting and electrofluidic display. a Structure and principle of electrowetting display. (i) Without any applied voltages, a colored oil film covers the pixel. (ii) When a voltage (~ 10 V) is applied, the oil film is contracting and makes the pixel transparent. b Schematic of an electrofluidic cell without a top plate. c Pixel array of electrowetting display with yellow dye based on alkylated pyrazole azo structure. d Images of electrofluidic pixels (square type and hexagonal type). Time-lapse images of a 500-um-square pixel is displayed. e Electrowetting based E-paper display by GR8 Optoelectronics Ltd. f Electrowetting based display demo by Liquavista
(Figure reproduced from a [23], Copyright 2003, Springer Nature; b [25], Copyright 2012, The Society for Information Display; c [26], Copyright 2018, The Society for Information Display; d [24], Copyright 2009, Springer Nature; e Copyright 2017, Gr8; f Copyright Liquavista)