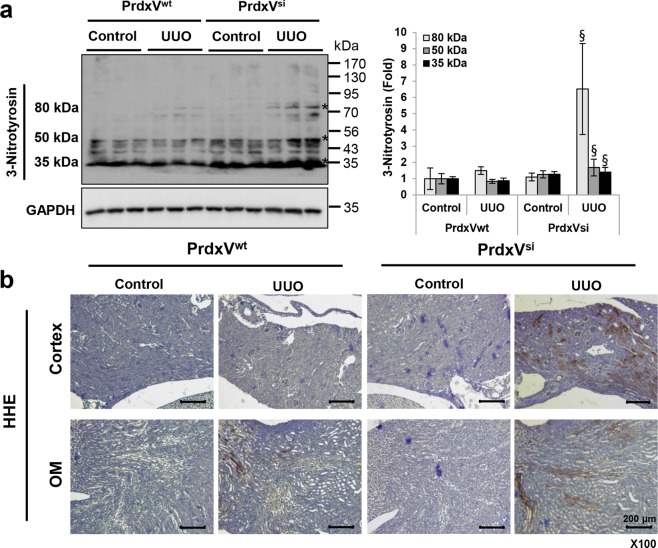
Figure 3.
The level of oxidative stress markers in UUO-induced PrdxVwt and PrdxVsi mouse kidney. As one of the major mechanisms of renal fibrosis induced by UUO, the level of oxidative stress was assessed in both PrdxVwt and PrdxVsi mouse kidneys. (a) The increased nitrotyrosine level in UUO-induced PrdxVsi kidney. The content of nitrotyrosine, as a protein oxidative marker, was analyzed by western blotting conducted with whole kidney lysates. Three major bands of different sizes were detected at 80 kDa, 50 kDa, and 35 kDa. GAPDH was used as an internal control. (b) The increased HHE level in UUO-induced PrdxVsi kidney. The content of HHE, as a lipid peroxidation marker, was analyzed by immunohistochemistry with a specific anti-HHE antibody. Image was magnified at x100, Bar = 200 μm. All values are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was measured using the one-way ANOVA with the Fisher least significant difference post-test. §p < 0.05; PrdxVwt vs. PrdxVsi in UUO group.