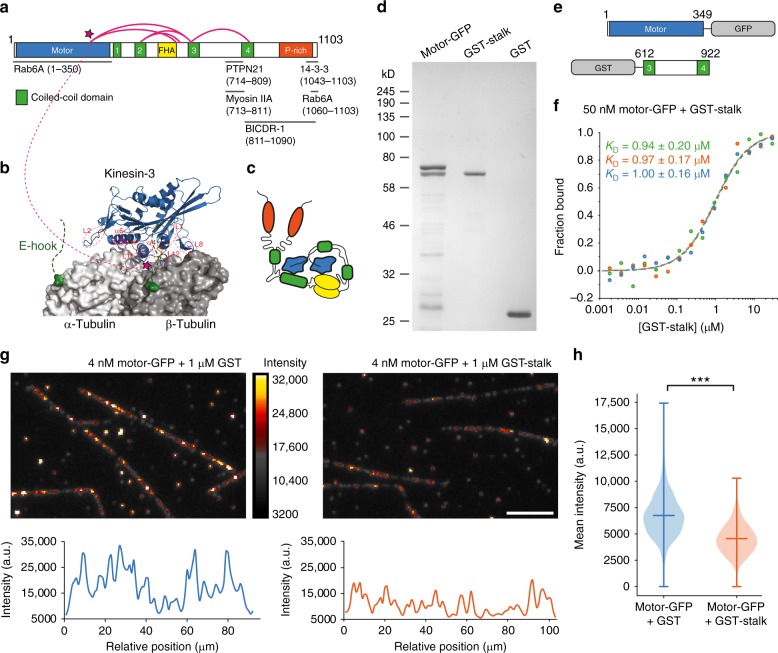
Fig. 2.
KIF1C is autoinhibited by intramolecular interactions of stalk and motor domain. a Schematic primary structure of KIF1C with motor domain (blue), coiled-coil domains (green), FHA domain (yellow), and Proline-rich domain (orange). Crosslinks identified using mass spectrometry after treatment with BS3 or EDC are shown as magenta loops. Published binding sites for KIF1C interactors are indicated below. See Figs. S2 and S3 for ion fragmentation of crosslinked peptides. b Motor domain of related KIF1A on tubulin. The region in the motor domain that interacts with KIF1C stalk is indicated by magenta stars. c Hypothetical model of autoinhibited KIF1C conformation based on identified crosslinks. d Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel of purified KIF1C motor domain, stalk domain and GST control. e Schematic primary structure of KIF1C motor and stalk proteins used here. f Binding affinity measurements and Kd model fits from three microscale thermophoresis experiments probing the interaction of KIF1C motor domain with the stalk domain. g Representative TIRF images showing microtubule decoration of KIF1C motor domain in the presence of GST (control) and KIF1C tail domain. Scale bar 5 µm. Linescans of one of the microtubules from each field is shown below. h Quantification of mean intensity of KIF1C motor domain on microtubules. Distribution is shown together with mean and full extent of data. n = 690 and 659 microtubules, respectively, pooled from six experiments. *** indicates p = 10−99 (t-test)