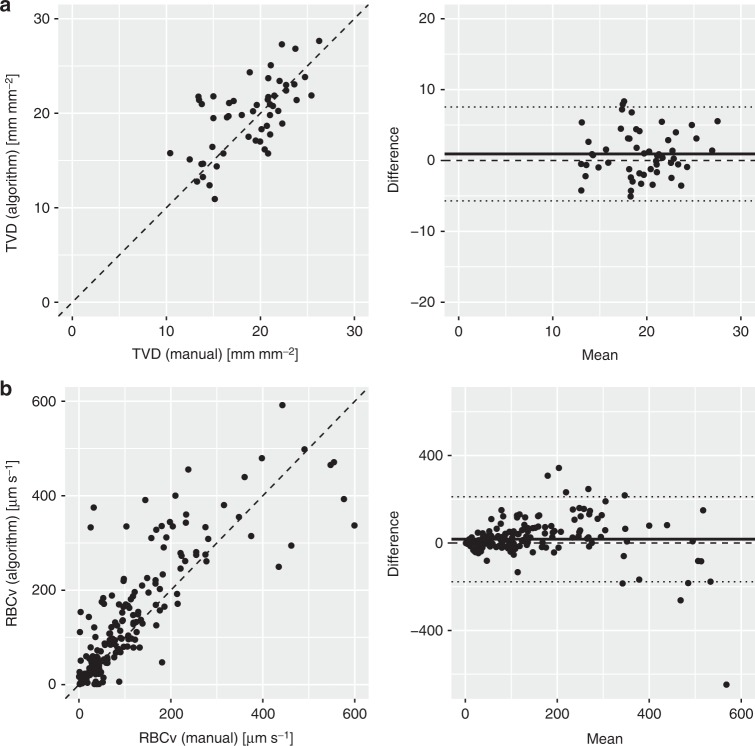
Fig. 4.
Good correlation was observed between manually measured and algorithm-based capillary TVD (a) and RBCv (b) in the septic shock model. TVD was compared by field of view in the septic shock and control groups (n = 53), and good correlation was observed (r = 0.7, p < 0.0001, bias 0.9 mm mm−2, level of agreement −5.7 to 7.5 mm mm−2, precision 3.3 mm mm−2, percentage error 6.7%). RBCv was compared by capillary in the septic shock group (n = 202), and good correlation was observed (r = 0.8, p < 0.0001, bias 17 µm s−1, level of agreement −117 to 212 µm s−1, precision 97 µm s−1). Dashed lines represent identity lines. In Bland–Altman analysis, solid line represents bias and dotted lines represent ±2σ levels of agreement. TVD total vessel density, RBCv red blood cell velocity