Figure 2.
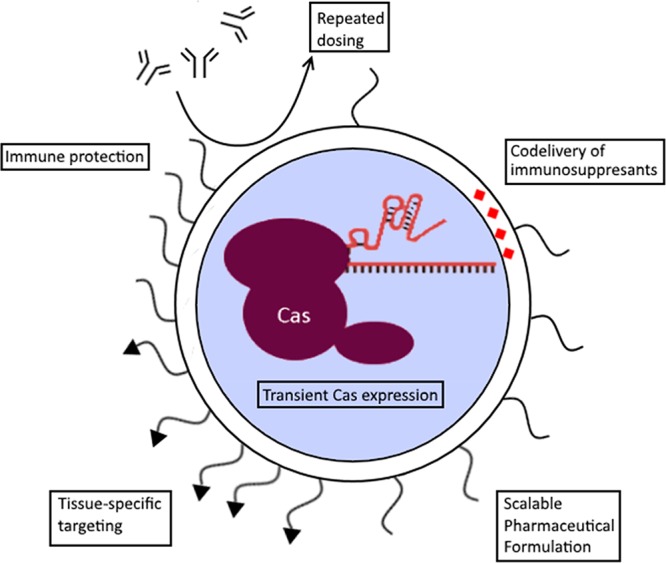
Advantages of synthetic vectors for CRISPR/Cas delivery using a lipid nanoparticle as example. The active RNP complex can be encapsulated by synthetic vectors, leading to a transient expression of the Cas protein. Addtionally, there is less risk of immune activation compared to viral vectors which allows for repeated dosing regimens, to potentially achieve cumulative gene editing.28 Most particles incorporate an inert component which shields the particle from immune detection, such as polyethylene glycol (PEG). These chains can be functionalized to target specific tissues or cells of interest using targeting ligands. Other cargoes can be codelivered as well, such as immune suppresant drugs. Finally, the chemical nature of the particle formation and modification allows for upscaling of the pharmaceutical production compared to biological production methods for viral particles.
