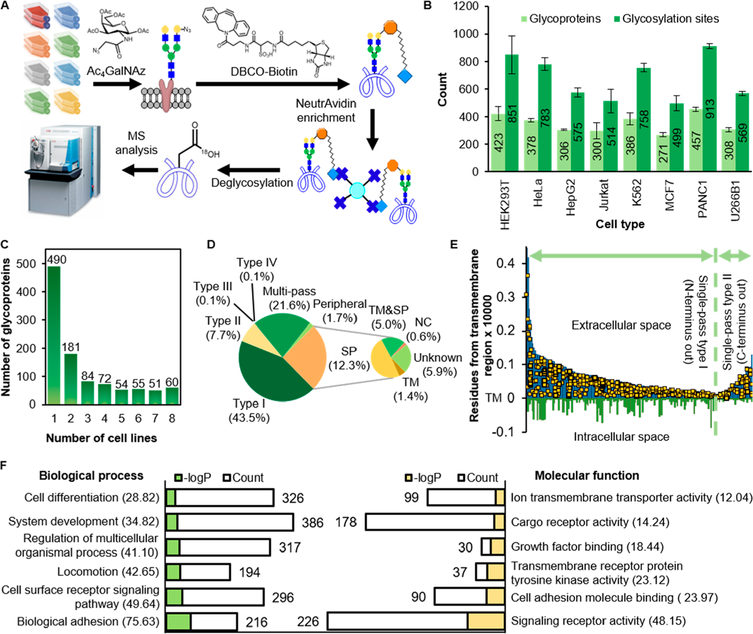
Figure 1.
Overview of global and site-specific analysis of cell-surface glycoproteins from eight popular types of human cells. (A) A diagram showing the experimental procedure. (B) Numbers of cell-surface glycoproteins and glycosylation sites identified from each cell type. The error bars represent one standard deviation from two biological duplicate experiments. (C) Number of cell-surface glycoproteins identified from multiple cell types. (D) Types of the identified surface glycoproteins. Types I−IV for single-pass membrane protein types I−IV, TM for transmembrane domain, SP for signal peptide, and NC for proteins entering the non-classical secretory pathway. (E) Single-pass types I and II suface glycoproteins from K562 cells are aligned against TM. Yellow dots represent the identified glycosylation sites. (F) Protein clustering of all identified surface glycoproteins based on biological process and molecular function. The number in the parentheses show the −logP values.