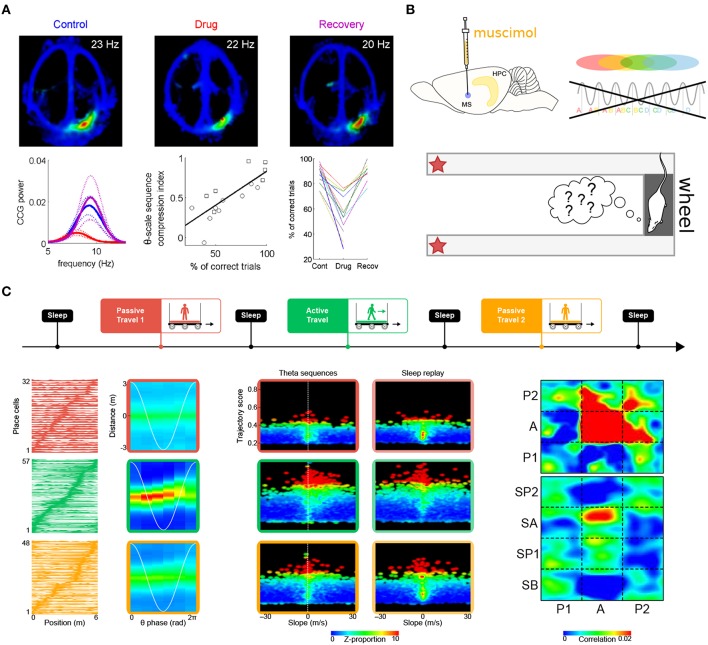
Figure 6.
Theta sequences and memory. (A) Selective perturbation of phase precession, but not firing maps, by injection of cannabinoid receptor agonist CP55940 induces performance deficits in a spatial memory task. Top. Firing maps for an example place cell recorded in control (left), drug (center), and recovery (right) conditions. Bottom left. Average power of the cross-correlograms for all neuron pairs with overlapping fields during control (blue), drug (red), and recovery conditions (magenta; dotted lines: s.e.m.) Bottom center. Correlation between behavioral performance (percentage of correct trials) and theta-scale sequence compression index in one rat. The different symbols refer to data obtained in two different experiments. Bottom right. Average performance (correct trials) for all sessions and rats. (B) Medial septum inactivation by muscimol infusion impairs theta sequences and behavioral performance. (C) Perturbation of theta sequences impairs subsequent sleep replay. Top. Experimental protocol. The rats traveled on a model train. In successive sessions, a miniature treadmill was either turned off (passive travel; red and yellow) or on (active travel; green) to selectively disrupt or maintain theta sequences, while leaving behavioral timescale sequences intact. Bottom left. Firing fields (left column) remained stable in all conditions (red, green and yellow curves), but theta sequences (right column) emerged only during active travel (green box). Bottom center. Trajectories represented by hippocampal sequences were assessed using a combination of measures, namely trajectory score (linearity) and slope (velocity). During passive travel and subsequent sleep (red and yellow boxes), a very low proportion of both theta and replay sequences emerged in the hippocampal network (upper right quadrants are mostly black). On the contrary, during active travel and subsequent sleep (green boxes), a dramatically higher number of theta sequences and replay events were observed (red dots in upper right quadrants). Bottom right. Similarity of theta and replay sequences (P1, P2: passive travel sessions; A: active travel session; SA, SP1, SP2: sleep following respective travel sessions). Theta sequences were clear and self-consistent only during active travel (red zone at [A,A]). Sleep replay mirrored theta sequences only following active travel (red zone at [A,SA]). Panel (A) adapted from Robbe and Buzsáki (2009); panel (C) adapted from Drieu et al. (2018), with permission from AAAS.