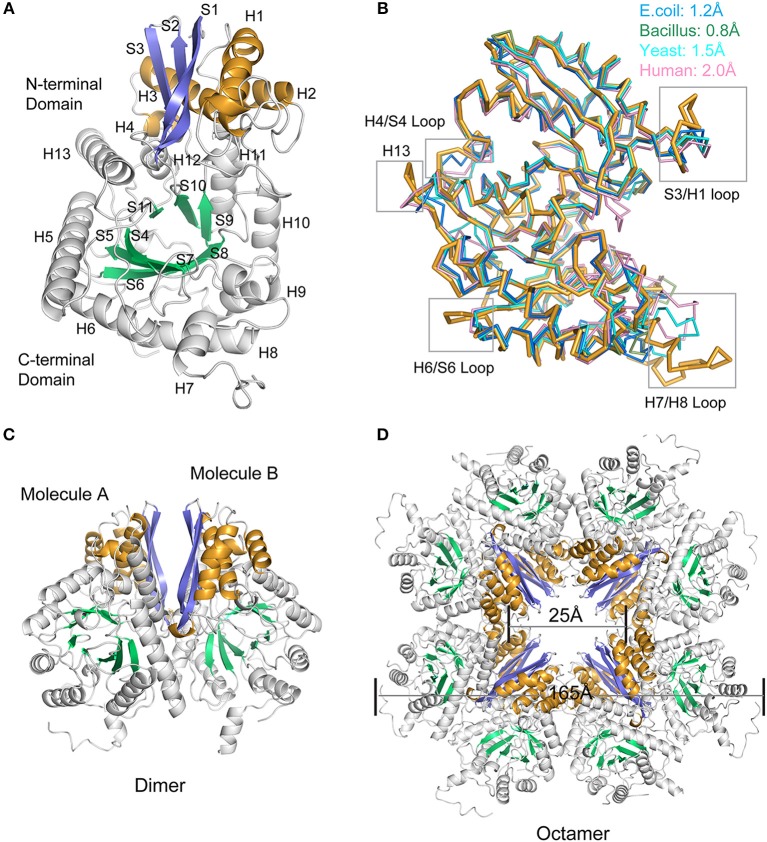
Figure 3.
Overall structure of Mhp Eno. (A) Structure of the protomer Mhp Eno. The β-strands and α-helices are sequentially numbered; “S” stands for β-strand, and “H” stands for α-helix. The β strands of the N-terminal domain and C-terminal domain are indicated in slate (S1-S3) and green cyan (S4-S10) colors, respectively. The α-helices of the N-terminal domain and C-terminal domain are indicated in bright orange (H1-H4) and white (H5-H13), respectively. (B) Structural comparisons between Mhp Eno and enolases from human (pink, PDB ID: 3B97), yeast (cyan, PDB ID: 3ENL), E. coli (blue, PDB ID: 1E9I), and Bacillus subtilis (green, PDB ID: 4A3R). All structures are shown in a ribbon format. Mhp Eno is shown in bright orange. The structure deviations are indicated at the top. The regions of Mhp Eno that show noticeable differences are marked by gray boxes. (C) Overall structure of the Mhp Eno dimer unit. (D) Overall structure of the Mhp Eno octamer. The diameters of Mhp Eno and the tunnel are indicated.