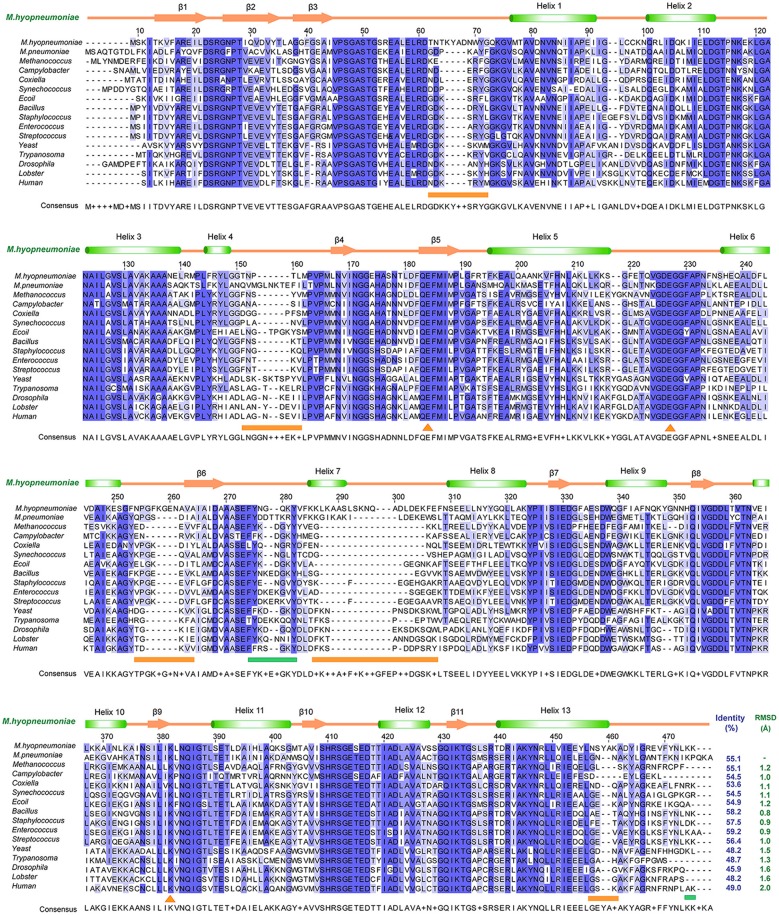
Figure 4.
Structural and sequence alignments between Mhp Eno and other enolases. The sequence identities and structural deviations are shown at the end of each sequence. The second structure of Mhp Eno is above the alignment. The regions that show notable differences are indicated with orange lines at the bottom of the alignment. The plasminogen-binding regions are marked by green lines at the bottom of the sequence. The sequences or structures are from M. pneumoniae (Mycoplasma pneumoniae, GenBank ID: WP_010874963.1), Methanococcus (Methanococcus jannaschii, PDB ID: 2PA6), Campylobacter (Campylobacter jejuni, PDB ID: 3QN3), Coxiella (Coxiella burnetii, PDB ID: 3TQP), Synechococcus (Synechococcus elongatus, PDB ID: 4ROP), E. coli (PDB ID: 1E9L), Bacillus (Bacillus subtilis, PDB ID: 4A3R), Staphylococcus (Staphylococcus aureus, PDB ID: 5BOF), Enterococcus (Enterococcus hirae, PDB ID: 1LYX), Streptococcus (Streptococcus pneumonia, PDB ID: 1W6T), Yeast (PDB ID: 3ENL), Trypanosoma (Trypanosoma brucei, PDB ID: 1OEP), Drosophila (PDB ID: 3WRO), Lobster (PDB ID: 1PDZ), and Human (PDB ID: 3B97).