Figure 2.
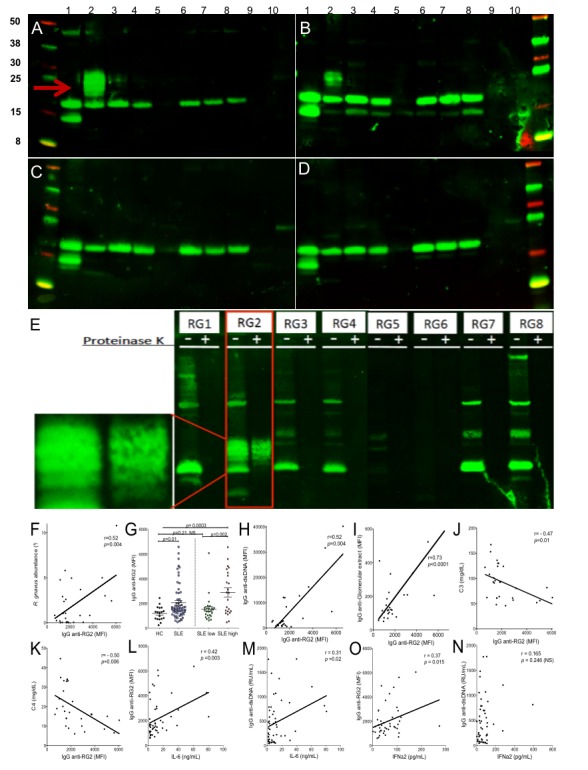
Patients with LN have serum IgG that recognise RG2 strain-restricted non-protein antigen(s) and that levels correlate with scores forlupus disease activity. Immunoblot results for IgG from (A) patient with LN (S-134), (B) patients with LN (S-047), (C) patient with non-active lupus (S-096) and (D) healthy control (CTL23). Bacterial extracts were prepared with nuclease and lysozyme treatment; lanes 1–8 represent R. gnavus RG1-RG8 strains (see online supplementary table 4), and lanes 9 and 10 contain extracts from gut commensal species, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron and Prevotella copri. After electrophoretic transfer, replicate membranes were incubated with different sera at 1:100 dilution, with detection for human IgG deposition. Only patients with highly active lupus had serum IgG that recognised the oligomeric antigenic band in RG2 (red arrow) that was not detected in other RG strains. (E) Immunoblot of human gut isolated strains of R. gnavus, RG1-RG8. For each strain, molecular species were electrophoretically separated side-by-side, after nuclease and lysozyme treatment (left lane) and after additional thorough proteinase K treatment (right lane). Reactivity for serum IgG from patient S-134 with active LN is shown, with the serum tested at 1:100. Inset shows magnified view of non-protein oligomeric bands in RG2 extract, which are also seen in panels A and B. (F) In patients with SLE, RG faecal abundance by 16S rRNA analysis correlates with the levels of serum IgG anti-RG2 antibody. (G) Levels of serum IgG anti-RG2 in individual patients with lupus in the NYU cohort were compared with unaffected adults (see Methods section). Patients with SLE with high disease activity (SLEDAI ≥8) had higher levels of anti-RG2 IgG antibodies than healthy controls and than SLE with low disease activity. (H) Levels of serum IgG antinative DNA directly correlate with IgG anti-RG2 antibodies. Results from multiplex assay using extracts treated with lysozyme and a broad endonuclease, which was separately coupled to a set of paramagnetic beads (Luminex) in parallel with other antigens. (I) Levels of IgG anti-RG2 directly correlate with IgG to an extract of human glomeruli. Results from multiplex assay. (J) Levels of serum C3 inversely correlated with levels of serum lupus IgG anti-RG2 antibodies in patients with SLE. (K) Levels of serum C4 inversely correlated with levels of serum lupus IgG anti-RG2 antibodies in patients with SLE. (L) IgG anti-RG2 levels strongly correlate with serum IL-6 levels. (M) Levels of IgG anti-dsDNA, determined by commercial ELISA (INOVA), have only a modest correlation with serum IL-6 levels. (N) IgG anti-RG2 levels correlate with IFNα2 levels, determined by commercial bead-based assay (Luminex). (O) Levels of IgG anti-dsDNA antibodies do not correlate with serum IFNα2 levels. IgG anti-DNA and RG2 levels were measured by in-house custom bead-based assays. C3 and C4 were measured with commercial ELISA, while cytokines were measured by commercial bead-based assays. Significance was based on Mann-Whitney test or Spearman correlations. LN, lupus nephritis; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; SLEDAI, SLE disease activity index.
