Figure 9.
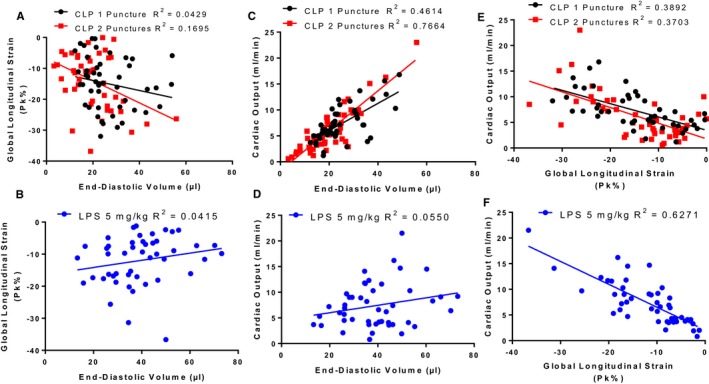
Preload and systolic dysfunction differentially contribute to reduced cardiac output between CLP and LPS sepsis models. A and B, No correlation between end‐diastolic volume and global longitudinal strain for echocardiogram measurements taken throughout the CLP1P, CLP2P, (A) and LPS (B) protocol. C and D, Significant correlation between end‐diastolic volume and cardiac output for CLP1P and CLP2P (C) but not LPS (D) sepsis model. E and F, Significant correlation between global longitudinal strain and cardiac output for both CLP (E) and LPS (F) models. Data points are representative of measurements from 24 mice at baseline, 2, 4, 6, 12, and 24 hours after sepsis induction. n=48 measurements for CLP1P, n=46 measurements for CLP2P, n=47 for LPS measurements 5 mg/kg. CLP indicates cecal ligation and puncture; LPS lipopolysaccharide.
