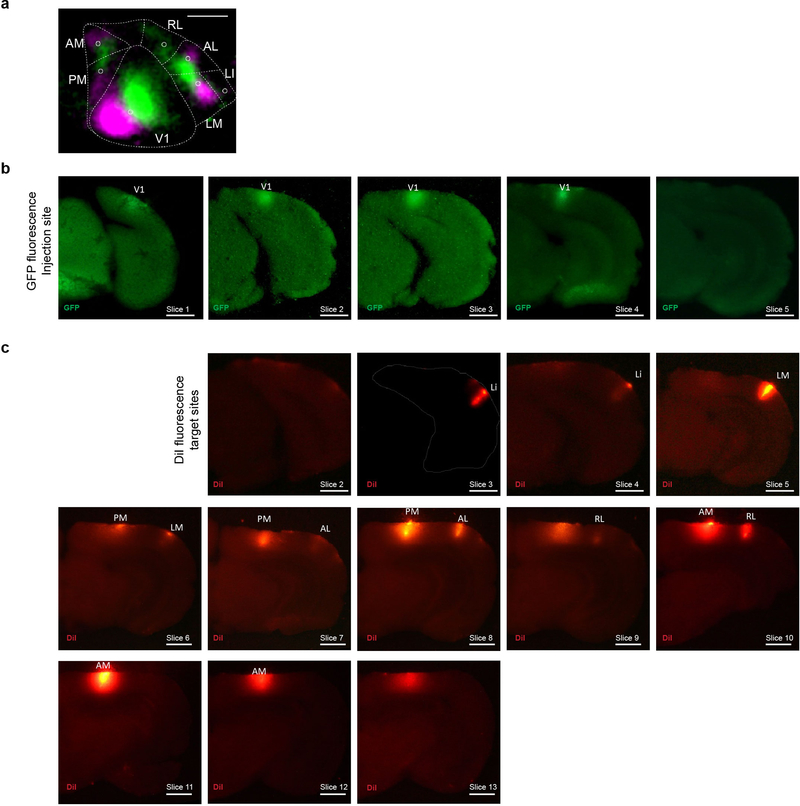
Extended Data Figure 9: MAPseq dissection strategy.
We identified the to-be-dissected high-er visual areas by performing intrinsic imaging of visual cortex in response to stimuli at different positions in the contralateral visual field and mapping the resulting changes in intrinsic signals. (a) A representative retinotopic map, with responses to the two 25° visual stimuli pseudocolored in green and magenta (stimulus 1 position: 90° azimuth, 20° elevation; stimulus 2 position: 60° azimuth, 20° elevation). Based on this map, we fluorescently labelled retinotopically matched positions in the to-be-dissected cortical areas with a DiI stab (white circles). Putative borders between the higher visual areas are indicated in dashed lines for orientation. Scale bar = 1 mm. N=4 animals. (b) The MAPseq virus injection site is discernible in consecutive frozen 180 m thick coronal sections, using GFP fluorescence. Scale bar = 1 mm. (c) DiI injections targeted to matched retinotopic positions in six target areas identified by intrinsic signal imaging. DiI epifluorescence images of each 180 m thick slice are shown, and dissected areas are labeled. Scale bar = 1 mm.