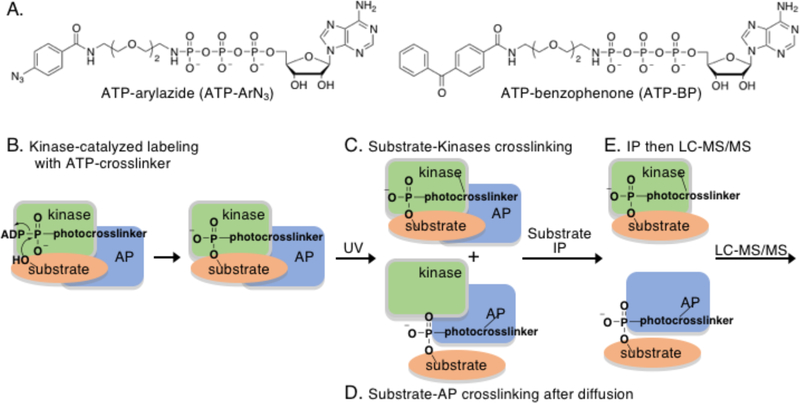
Figure 1.
A) The chemical structures of the two ATP-crosslinking analogs used in this work. B) Kinase-catalyzed labeling of a substrate with the ATP-crosslinking analog forms a substrate product with the crosslinker group covalently attached. C) Simultaneous UV irradiation results in covalent conjugation of the kinase and substrate through the photocrosslinking group. D) Because the kinase-substrate interaction is transient, a large fraction of the substrate is expected to dissociate and diffuse away from the kinase after catalysis. UV irradiation after diffusion will result in covalent attachment of the substrate to any substrate- and/or kinase-associated protein (AP). E) After kinase-catalyzed crosslinking, immunoprecipitation (IP) of the substrate protein will isolate both the attached kinase and associate proteins, which can be characterized by LC-MS/MS.