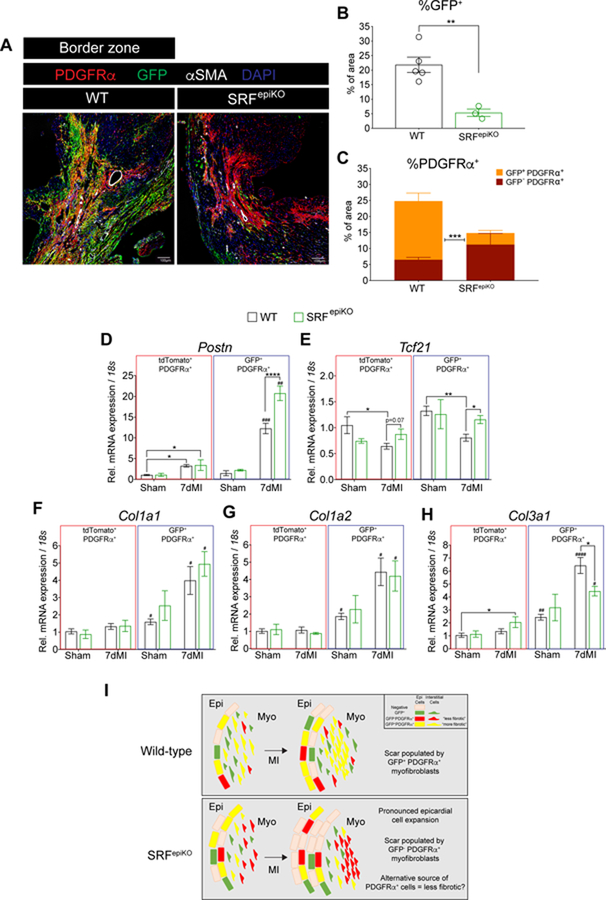
Figure 7. Infarct re-cellularization requires SRF expression in EPDCs.
(A) Labeling of Wt1 lineage derived cells (GFP+) and PDGFRα+ cells in WT and SRFepiKO mice. (B) Quantitation of GFP protein expression in the BZ regions and 14 days post MI (% of area). (C) Distribution of GFP−/PDGFRα+ and GFP+/PDGRα+ protein expression. Gene expression analysis of GFP+/PDGFRα+ and tdTomato+/PDGFRα+ cells isolated by FACS from sham surgical mice and mice subjected to MI for 7 days. (D) Postn, (E) Tcf21, (F) Col1a1, (G) Col1a2, and (H) Col3a1. (I) Schematic of proposed cellular mechanism of epicardial-derived fibrosis in the adult heart after MI. In non-injured conditions, WT mice show maintenance of epicardial-derived PDGFRα+ myofibroblasts, which expand in response to MI. In contrast, SRFepiKO mice show reduced investment of epicardial-derived PDGFRα+ cells at baseline and following MI. Alternative to the response in WT mice, the scar is re-populated with GFP−PDGFRα+ myofibroblasts, a nonepicardial cell lineage that is likely descended from an alternative “less fibrotic” cell lineage. EPI = epicardium. MYO = myocardium. MI = Myocardial Infarction.
Scale bar (A) = 40µm.
* p<0.05, ** p<0.01, ****p<0.0001.
# p<0.05, ## p<0.01, ### p<0.001, #### p<0.0001: GFP+/PDGFRα+ versus tdTomato+/PDGFRα+.