Figure 1.
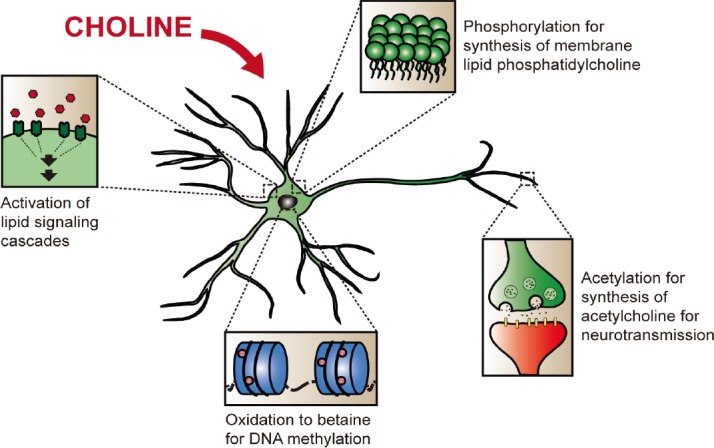
The main physiological roles of choline in that may modulate plasticity in neuronal cells.
Choline can be phosphorylated as part of the synthesis pathway of phosphatidylcholine, for the synthesis of neuronal membranes. It can also be acetylated to form acetylcholine for use in neurotransmission. Oxidation of choline gives betaine, an intermediate in the production of labile methyl groups. Choline and its metabolites can further participate in cellular lipid signaling mechanisms.
