Figure 1.
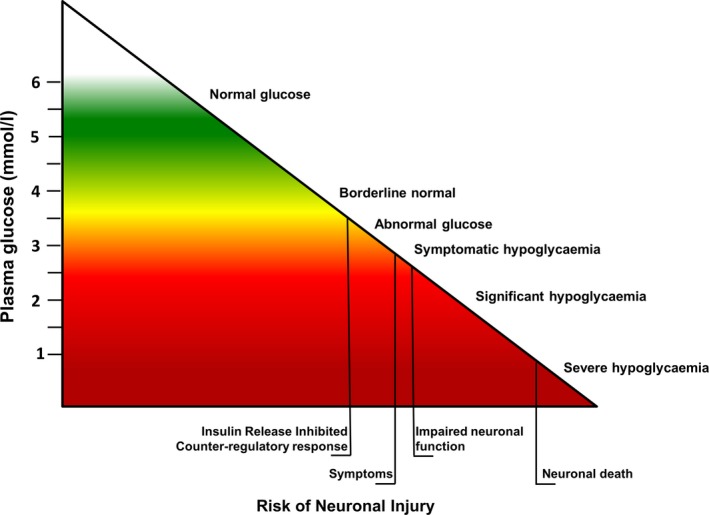
Relationship between plasma glucose and risk of neuronal injury in normal children: as glucose levels decrease, the risk of hypogycaemia‐induced neuronal damage increases. While there is no numerical definition of hypoglycaemia in children, the inverse correlation between glucose and risk supports a pragmatic clinical approach to keep glucose levels near the normal range to prevent long‐term brain damage.
