Figure 1.
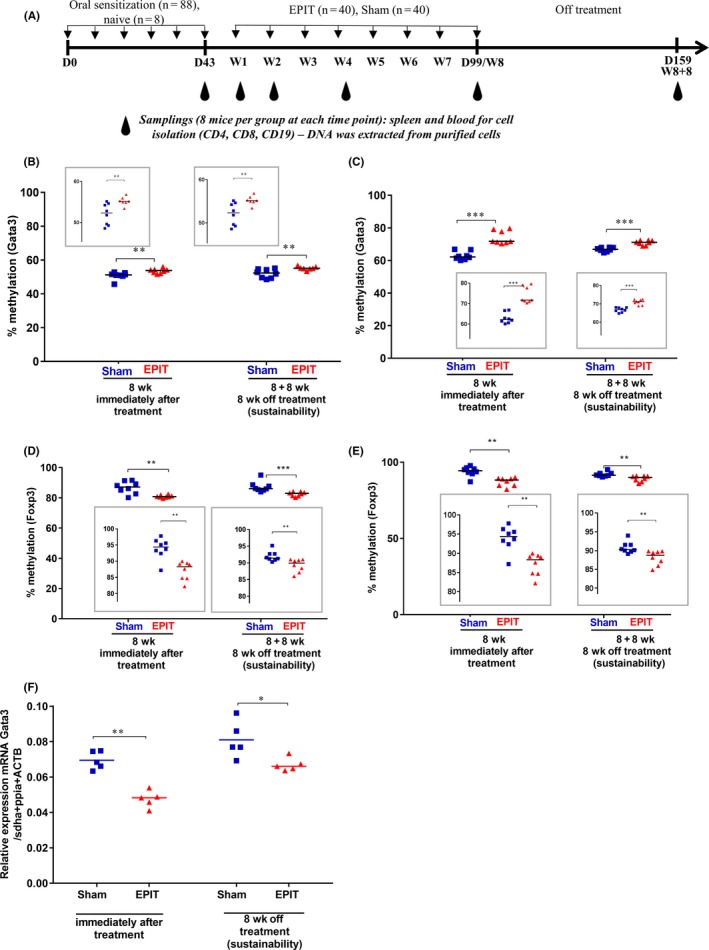
Epicutaneous immunotherapy (EPIT) induces DNA hypermethylation of Gata3 and hypomethylation of Foxp3 in CD4+ cells purified from spleen and blood during EPIT, which is accompanied by a reduction of Gata3 mRNA expression in CD4+ cells purified from the spleen. A, Experimental design for the methylation analysis of DNA isolated from CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and CD19+ B cells (of spleen and blood) occurring during EPIT for sensitized mice epicutaneously treated using a patch loaded with peanut protein extract (EPIT) or a placebo (Sham). Analysis of the methylation levels of the Gata3 promoter in CD4+ cells isolated from (B) spleen and (C) whole blood at week 8 (8 wk) of EPIT and 8 weeks after the end of EPIT (8 + 8 wk). Analysis of the methylation levels of Foxp3 in CD4+ cells isolated from (D) spleen and (E) whole blood at week 8 (8 wk) of EPIT and 8 weeks after the end of EPIT (8 + 8 wk). (F) Measurement of the expression level of Gata3 mRNA by RT‐qPCR. Results are expressed as individual data and median. Differences between groups were analyzed by a Kruskall‐Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparison test. *P < .05, **P < .01 and ***P < .001
