Figure 7.
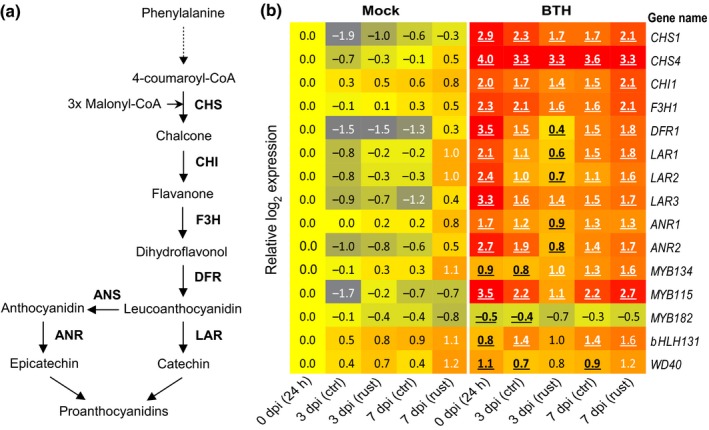
Transcriptional upregulation of genes encoding transcription factors and enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of proanthocyanidins (PAs) in black poplar treated with benzothiadiazole (BTH). (a) Flavonoid pathway leading to the formation of catechin and PAs. (b) Relative expression of PA biosynthesis genes and MYB transcription factors regulating this pathway. Transcript levels were measured by quantitative reverse transcription PCR using two technical replicates per sample. Transcripts of each gene were normalized to ubiquitin expression. The heat map was generated using the average values (log2‐transformed) of five biological samples per treatment. Time‐point data (mock vs BTH) were analyzed using a Student's t‐test. Bold underlined values are significantly different between BTH‐ and mock‐treated samples (P ≤ 0.05). CHS, chalcone synthase; CHI, chalcone isomerase; F3H, flavanone 3‐hydroxylase; DFR, dihydroflavonol reductase; FLS, flavonol synthase; LAR, leucoanthocyanidin reductase; ANS, anthocyanidin synthase; ANR, anthocyanidin reductase. Note that MYB134 and MYB115 positively regulate PA synthesis in association with the basic helix–loop–helix enzyme bHLH131 (James et al., 2017). MYB182 acts as a negative regulator of PA synthesis in poplar (Yoshida et al., 2015).
