Figure 2.
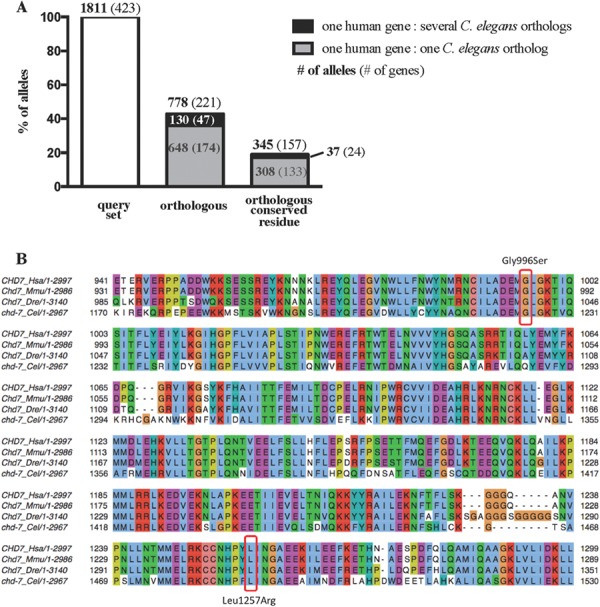
Detection of conserved ASD-associated missense residues in C. elegans. (A) For each missense allele, the C. elegans ortholog of the corresponding human gene was identified using the Ensembl Compara method. Each Ensembl ortholog pair was underpinned by a protein multiple-sequence alignment, which can be used to identify the putative orthologous C. elegans amino acid for a given human amino acid. Forty-three percent of the human missense variants had at least one C. elegans ortholog. A total of 130 of the 778 orthologous missense variants had more than one C. elegans ortholog (black bar). Overall, only 19% of the missense residues were orthologous and conserved in C. elegans. (B) Section of the protein multiple alignment for human (Hsa) CHD7 and its orthologs in mouse (Mmu), zebrafish (Dre) and C. elegans (Cel). Residues in the alignment have been colored by JalView (PMID: 19151095) using the Clustal X coloring scheme. Circled are two ASD-linked missense variants in CHD7 that occur in a highly conserved region across all the species.
