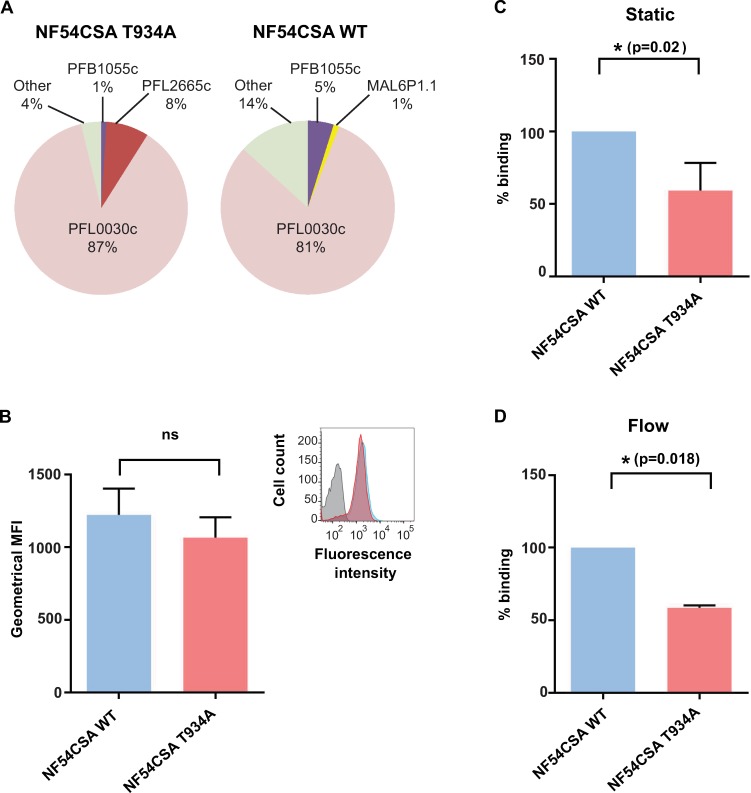
Fig 5. Characterisation of transgenic NF54CSA T934A parasites.
(A) VAR2CSA transcription profile of wild-type and T934A NF54CSA IEs after reselection on VAR2CSA antibodies. Transcriptional levels of each var genes were normalised with the housekeeping gene, seryl-tRNAtransferase. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of wild-type and T934A NF54CSA IEs after panning with anti-VAR2CSA antibodies. CSA-selected IEs were labelled with anti-VAR2CSA antibodies. Geometric means of fluorescence intensities of 2 independent experiments and corresponding standard deviation are indicated. (C) Static cytoadhesion assay of wild-type and T934A NF54CSA IEs. The effect of T934A mutation on IEs binding was assessed in static assay on CSA-coated petri dishes. Numbers of NF54CSA T934A IEs attached were counted in 5 random fields, and results were expressed as percentage binding compared with wild-type NF54CSA IEs (100% binding) from 3 independent experiments. Blue and red histograms correspond, respectively, to the wild-type and transgenic parasite strains. (D) Effect of VAR2CSA T934A mutation on IEs binding was assessed in a flow-based adhesion assay. IEs were flowed over decorin-coated microslides. A shear stress of 0.05 Pa was applied for 10 min. Numbers of adherent IEs were counted in 6 positions, and results were expressed as percentage binding compared with wild-type NF54CSA IEs (100% binding). Blue and red histograms correspond, respectively, to the wild-type and transgenic parasite strains. Numerical values that underline the graphs are shown in S5 Data. CSA, chondroitin sulfate A; IEs, infected erythrocytes; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; NF54CSA, Plasmodium falciparum isolate NF54 selected for CSA adhesion; ns, not significant; VAR2CSA, variant surface antigen 2-CSA; WT, wild type.