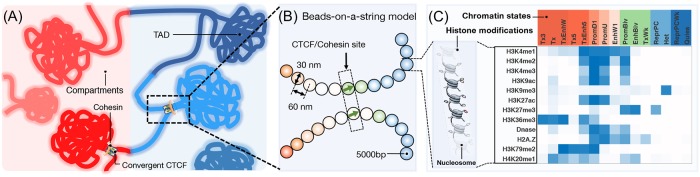
Fig 1. Overview of the key elements of the computational model.
(A) Illustration of genome organization at various length scales that includes the formation of CTCF mediated chromatin loops, TADs, and compartments. (B) A schematic representation of the computational model that highlights the assignment of chromatin states and CTCF binding sites. Chromatin states for each bead—a 5kb long genomic segment—are derived from the combinatorial patterns of histone marks. They are shown in part (C) as a heat map with darker colors indicating higher probabilities of observing various marks.