Figure 1. Fetal ethanol exposure decreased intracellular zinc levels in the AMs from newborn pups but was restored by zinc treatment.
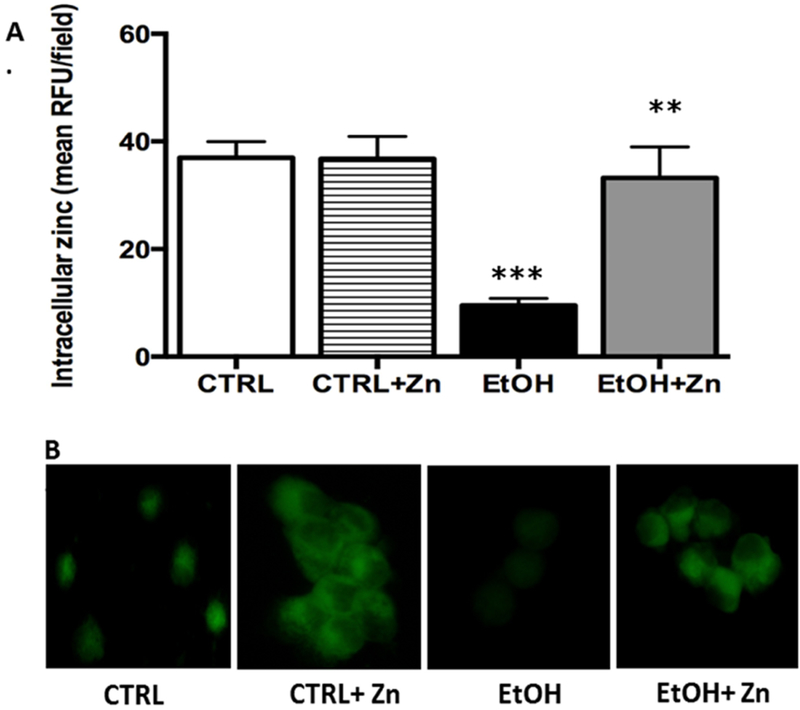
Dams were fed the control or ethanol diet during pregnancy and the AMs from the pups were isolated by lavage on the first day of life. The AM were cultured for 16 h with some AMs treated with media containing 25 μM zinc acetate. After incubation, FluoZin-3AM was added to the media (30 min.) before the cells were washed and fixed for confocal microscopy. RFUs were quantified by computerized analysis of the confocal fluorescent images and the bar heights represent the mean RFU/field ± S.E.M. from at least 6 different litters (A). Representative fluorescent images are shown for each condition (B). CTRL = control group; CTRL + Zn = control AMs treated in vitro with zinc acetate; EtOH = ethanol group; and EtOH + Zn = ethanol AMs treated in vitro with zinc acetate. *** denotes p = 0.05 when compared to the CTRL group and ** denotes p ≤ 0.05 when comparing the ETOH and ETOH + Zn groups.
