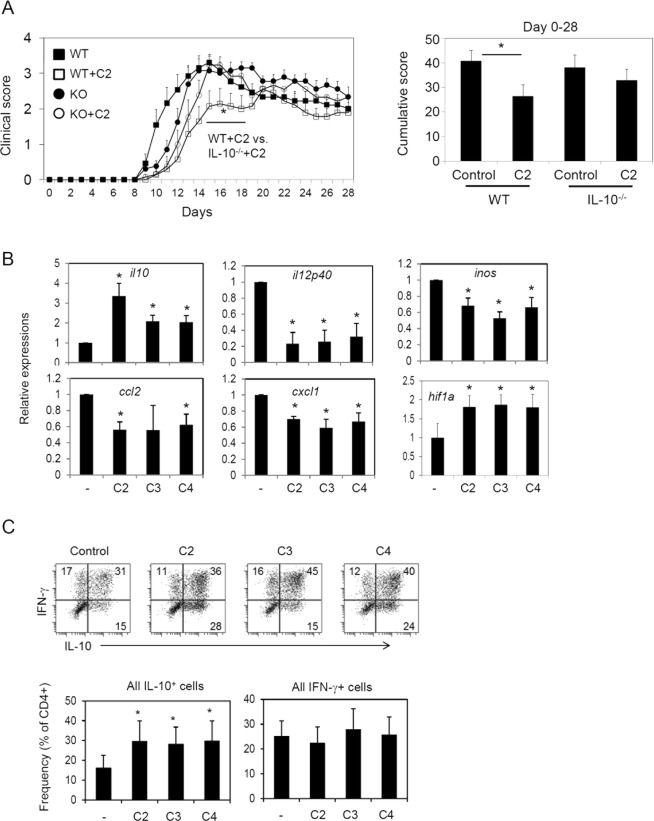
Figure 3.
Role of IL-10 in SCFA-mediated suppression of EAE, and induction of tolerogenic antigen presenting cells by SCFAs. (A) C2 effect on EAE development in WT versus IL-10-deficient mice. Wild type and IL-10-deficient mice were on C2 drinking water during the whole experimental period. Immunization with MOG35–55 peptide was performed 2–4 weeks after the mice were on C2 water. Representative and pooled data obtained (mean ± SEM, n = 4–15) from 3–4 independent experiments are shown. *Significant differences between indicated pairs (P < 0.05). (B) mRNA expression of indicated genes by CNS-tissue derived glial cells cultured in the presence and absence of SCFAs (C2 at 10, C3 at 1, and C4 at 0.5 mM). The glial cells were established for 4 days in vitro and activated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) and IL-17 (25 ng/ml) for 3 days. (C) IL-10 and IFN-γ expression by CD4+ T cells that were co-cultured in the presence and absence SCFA-treated glial cells. The glial cells that were activated as in panel B were co-cultured with naïve CD4+ T cells in the presence of SEB for 5–6 days, and the frequency of IL-10+ and IFN-γ+ T cell were examined. Representative and pooled data (mean ± SEM, n = 4–5) are shown. *Significant differences between indicated pairs (P < 0.05).