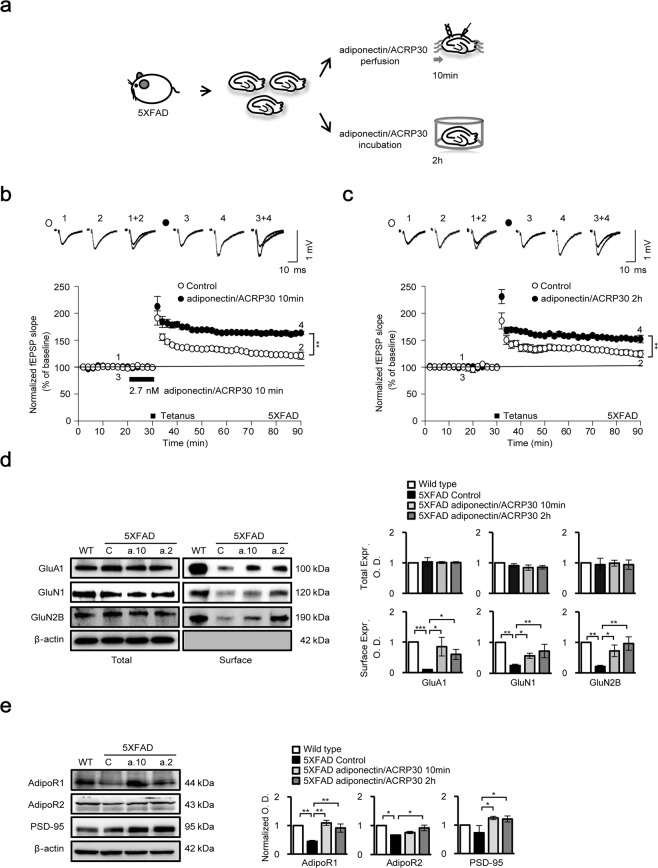
Figure 1.
Electrophysiological recordings in the CA1 hippocampal region, and ionotropic glutamate receptor, AdipoR1, AdipoR2 and PSD-95 protein expression after adiponectin/ACRP30 treatment. (a) Schematic diagrams of the experimental procedure and field recordings in hippocampal slices. (b,c) High-frequency stimulation (HFS; two trains of 100 Hz, 100 pulses) failed to induce LTP in 5XFAD mice (n = 4). However, HFS induced robust LTP in slices following adiponectin/ACRP30 perfusion (10 min) and incubation (2 h) (closed circles). (d) In vitro surface expression of GluA1, GluN1 and GluN2B decreased in the 5XFAD mouse hippocampus compared with that in wild-type mice; however, these decreases were reversed by adiponectin/ACRP30 treatment under both conditions (n = 3). No change in GluA1 (AMPA receptor subunit), GluN1 (NMDA receptor subunit) or GluN2B (NMDA receptor subunit) expression was observed (n = 3). (e) AdipoR1, AdipoR2 and PSD-95 protein levels were decreased in 5XFAD mouse hippocampus compared with those in wild-type mice; however, adiponectin/ACRP30 significantly increased protein levels under both treatment conditions. Data are expressed as means ± SEMs. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001; adiponectin/ACRP30 perfusion, 2.7 nM adiponectin/ACRP30 perfusion for 10 min; adiponectin/ACRP30 incubation, 2.7 nM adiponectin/ACRP30 incubation for 2 h; a.10, adiponectin/ACRP30 treatment for 10 min; a.2, adiponectin/ACRP30 treatment for 2 h.