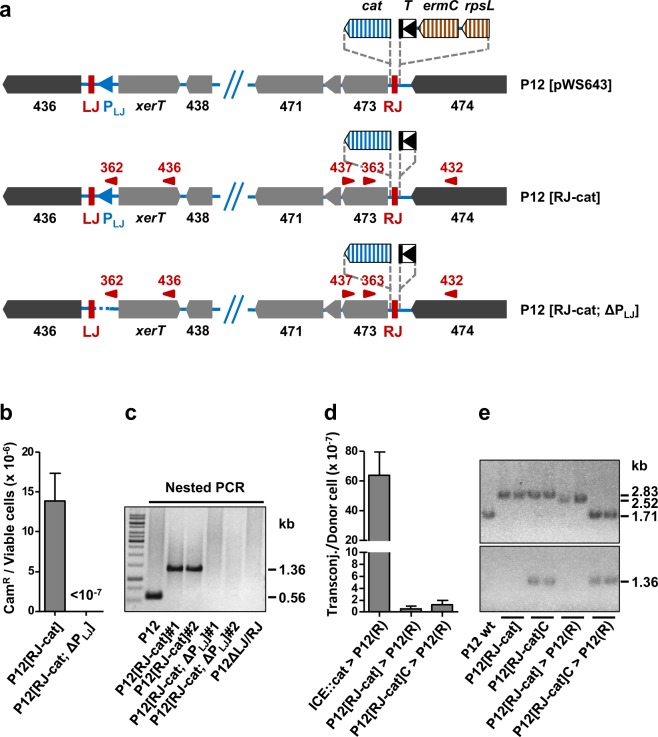
Figure 5.
ICEHptfs4 excision rates and transfer efficiencies. (a) Generation of marker-free chloramphenicol-selectable strains using the rpsL-erm counterselection strategy. First, a combination of an rpsL-ermC-T-HP1395 cassette outside of ICEHptfs4 and the promoterless cat cassette within ICEHptfs4 (plasmid pWS643) was introduced into a streptomycin-resistant P12 strain by selection for erythromycin resistance. In a second step, the rpsL-ermC marker cassette was removed by transformation with plasmid pWS649 lacking the rpsL-ermC markers, and selection for streptomycin resistance (resulting in strain P12 [RJ-cat]). Correct insertion of the terminator and the cat cassette was confirmed by sequencing. In a similar way, strain P12 [RJ-cat; ΔPLJ], additionally lacking the putative PLJ promoter activity upstream of xerT, was constructed by two consecutive transformations from P12 [RJ-cat]. (b) Excision rates of ICEHptfs4 from the chromosome was determined in P12 [RJ-cat] and P12 [RJ-cat; ΔPLJ] by plating serial dilutions on non-selective and on chloramphenicol-containing plates, respectively. Data represent average values from six independent experiments with standard errors of the mean. (c) Nested PCR with primer pairs WS436/WS437, and subsequently WS362/WS363, was performed from genomic DNA of the indicated strains. (d) Chloramphenicol-selected (P12 [RJ-cat]C) and non-selected colonies of P12 [RJ-cat] were provided with a ΔrecA::ermC mutation and subsequently used as donor strains for mating experiments with the recipient P12(R) (ΔmoeB::aphA-3). Transfer frequencies are indicated as chloramphenicol/ kanamycin double-resistant clones per viable donor cell. Data represent average values from at least three independent experiments including standard errors of the mean (n = 16, 3, and 3 from left to right). (e) Two clones each of strain P12 [RJ-cat] grown without chloramphenicol selection, or with chloramphenicol selection, and transconjugants obtained by mating either non-selected or chloramphenicol-selected P12 [RJ-cat] with P12(R) were characterized by PCR for the presence and properties of the ICEHptfs4 RJ region (primers WS432/WS437; upper panel), and for the circular product (primers WS362/WS363; lower panel). A P12 wild-type strain was used as a control. Sizes of the resulting PCR products are indicated on the right (2.83 kb: RJ with cat and T-HP1395; 2.52 kb: RJ with cat, but without T-HP1395; 1.71 kb: RJ without cat and T-HP1395; 1.36 kb: circular form including cat).