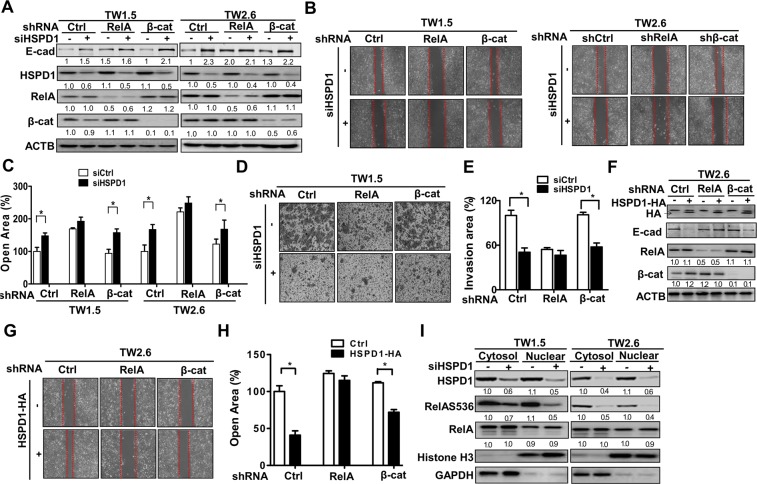
Figure 4.
Involvement of HSPD1 in RelA-mediated migration and invasion through phosphorylation of RelA at Ser536 in TW1.5 and TW2.6 cells. (A) The protein levels of RelA and β-catenin stable knockdown TW1.5 and TW2.6 cells harboring siRNAs against HSPD1 were analyzed. (B-C) The migration abilities of RelA and β-catenin stable knockdown TW1.5 and TW2.6 cells harboring siRNAs against HSPD1 were analyzed. (D-E) The invasion abilities of RelA and β-catenin stable knockdown TW1.5 cells harboring siRNAs against HSPD1 were analyzed. (F) The protein levels of RelA and β-catenin stable knockdown TW2.6 cells harboring an HA-tagged HSPD1 expression vector were analyzed. (G-H) The migration abilities of RelA and β-catenin stable knockdown TW2.6 cells harboring an HA-tagged HSPD1 expression vector were analyzed and quantified. (I) RelAS536 phosphorylation and RelA expression in both the cytoplasm and nucleus of TW1.5 and TW2.6 cells transfected with HSPD1 siRNA were analyzed. HSPD1 protein levels were analyzed by Western blot analysis. The transcriptional activity was measured by luciferase assay. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary information.