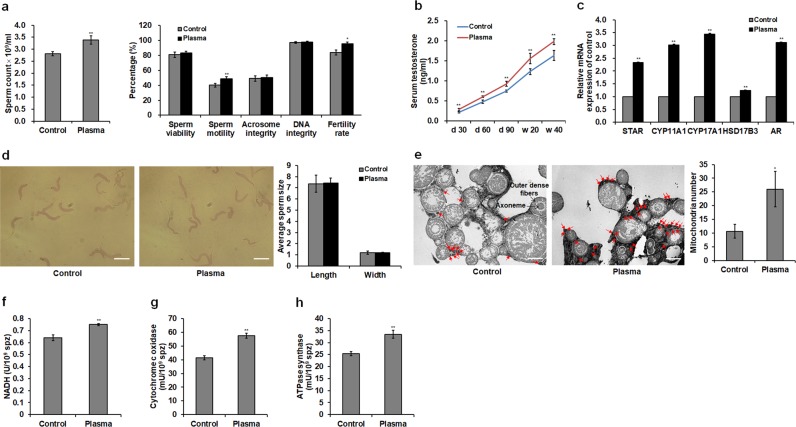
Figure 1.
Sperm quality, testosterone level, sperm structure, and mitochondrial respiratory enzyme level in the spermatozoa. (a) Sperm count, viability, motility, integrities of acrosome and DNA, and fertility rate in 40-week-old male chickens. Sperm quality of 20-week-old male chickens are shown in Supplementary Fig. S1. (b) Testosterone levels in the serum of male chickens on days 30, 60, and 90, and weeks 20 and 40. For the sperm quality and testosterone level, data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) (n = 10) of three replicates; n represents an individual chicken. (c) Relative mRNA levels of testosterone biosynthesis genes [steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (STAR), cytochrome P450 family 11 subfamily A member 1 (CYP11A1), cytochrome P450 family 17 subfamily A member 1 (CYP17A1), and hydroxysteroid 17-beta dehydrogenase 3 (HSD17B3)] and androgen receptor (AR) gene in the testis of 40-week-old male chickens. (d) Representative sperm optical microstructure and average sperm size in 40-week-old male chickens. Scale bar: 5.0 μm. (e) Representative ultrastructure of transverse section of spermatozoa and mitochondria number. Mitochondria located around the outer dense fibers of the sperm midpiece are photographed. The red arrow shows the mitochondrion. Scale bar: 2.0 μm. (f) Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide hydrogen (NADH) levels and activities of (g) cytochrome c oxidase and (h) ATPase synthase in the mitochondria of spermatozoa. For the mRNA level, mitochondrial number, and mitochondrial respiratory enzyme level, data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3) of three replicates; n represents an individual chicken. *p < 0.05 versus control; **p < 0.01 versus control, according to the one-way ANOVA with a least significant difference (LSD) test.