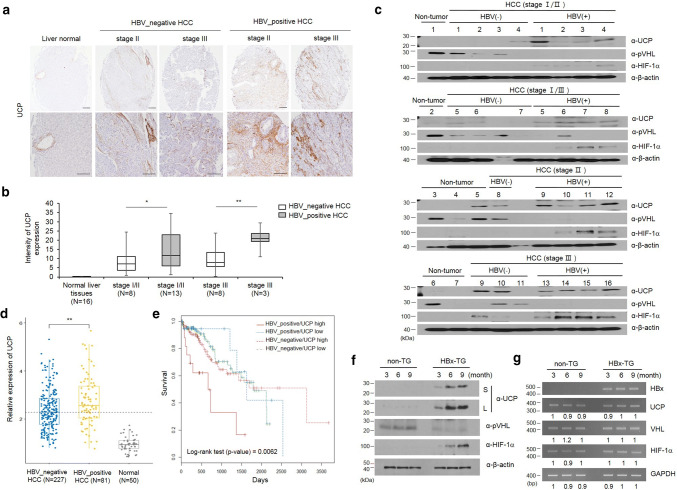
Fig. 1.
UCP is highly expressed in the liver tissues of HBx-transgenic mice and is frequently detected in HBV-positive HCCs. a The representative image shows that UCP was strongly expressed in late stage of HBV-positive HCCs compared to HBV-negative HCCs. b UCP staining intensity was quantified using Image J software. c We immunoblotted protein extracts from HBV-positive (+) or HBV-negative (−) HCC tissues of the indicated stages and from non-tumor tissues adjacent to or apart from HCC tissues as indicated. d The expression of UCP was assessed with liver hepatocellular carcinoma (TCGA-LIHC) RNA-seqv2 data (HTSeq-FPKM) and clinical datasheets were obtained from the TCGA data portal. e Overall survival rate was assessed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) of HBV-positive or HBV-negative patients. We prepared whole cell lysates or total RNAs from liver tissues of TG or non-TG mice at the indicated age and analyzed them by WB (f) or RT-PCR (g) as indicated. RT-PCR products were quantified by densitometry and the results are expressed relative to the band intensity of the first lane in b, which was arbitrarily defined as 1. S short exposure, L long exposure. We repeated the experiments of this figure twice; representative data are shown (i.e., *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01)