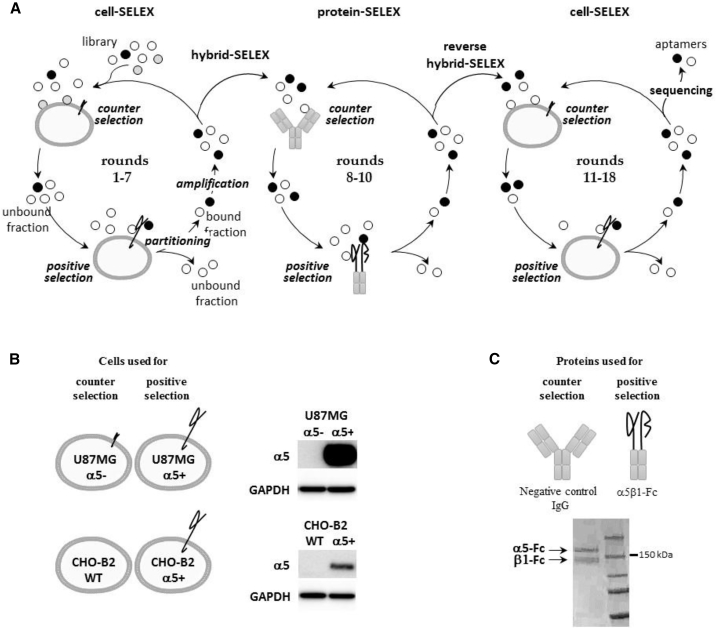
Figure 1.
SELEX Strategy
(A) Scheme of the cell- and protein-based SELEX strategy used for aptamer selection. Briefly, one round of SELEX first involves a selection step. The nucleic acid library is incubated with a target (positive selection), which can be preceded by counterselection to remove non-specific nucleic acid molecules. During the partitioning step, bound and unbound fractions are separated. The bound fraction is amplified to obtain an enriched pool for the next round of selection. First, cell-SELEX processes were performed (rounds 1–7), followed by protein-SELEX (rounds 8–10) and then by cell-SELEX (rounds 11–18). The combination of cell- and protein-based SELEX is called hybrid SELEX and reverse hybrid SELEX. At the end of selection, nucleic acid molecules were cloned and sequenced. Individual sequences are aptamers. (B) Description of cells used for counterselection and positive selection (rounds 1–7 and 11–18). On the right, western blots show the level of expression of α5 in the different cell lines used for the SELEX strategy. (C) Description of proteins used for counterselection and positive selection (rounds 8–10). Counterselection was also performed on protein-A Sepharose beads alone in rounds 8–10. Shown below is a denaturing SDS polyacrylamide gel loaded with the protein A-purified recombinant α5β1-Fc protein and Coomassie blue stained.