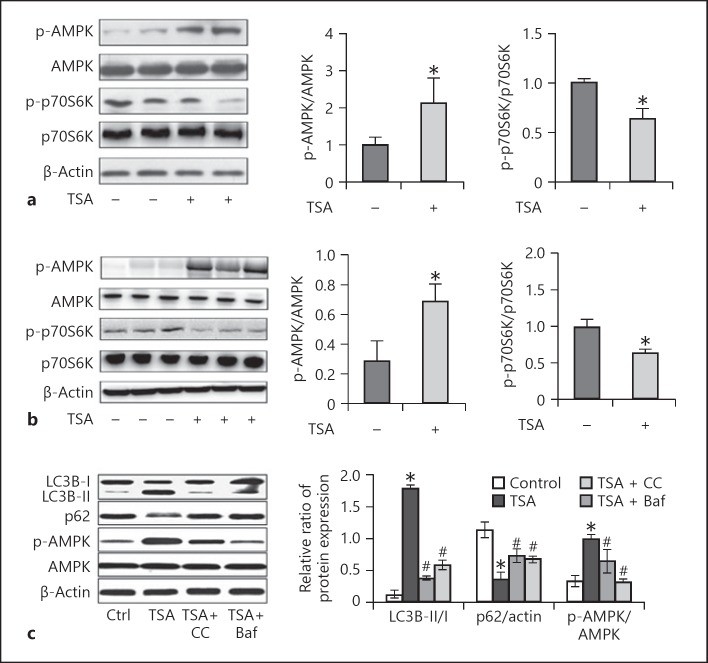
Fig. 8.
TSA activates AMPK and inactivates mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in Pkd1 mutant renal epithelial cells and mice. a Pkd1−/− cells were treated with TSA (0.1 μM) only for 8 days or not. After treatment, cells were collected for immunoblot analysis of p-AMPK, AMPK, p-p70S6K, and p70S6K. β-Actin was used as a loading control. Left: representative immunoblots. Right: densitometric analysis of p-AMPK and p-p70S6K signals after normalization with AMPK and p70S6K, respectively. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. * p < 0.05 vs. untreated group. b Pkd1−/− mice were injected with DMSO or a single dose of TSA (1 mg/kg, i.p., daily injection). Kidneys were collected 25 days after treatment for immunoblot analysis of p-AMPK, AMPK, p-p70S6K, and p70S6K. β-Actin was used as a loading control. Left: representative immunoblots. Right: densitometric analysis of p-AMPK and p-p70S6K signals after normalization with total AMPK and p70S6K, respectively. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. * p < 0.05 vs. untreated group. c Pkd1−/− mice were pretreated with TSA and recovered for 3 days, and were then treated with Baf or CC. The expression of p-AMPK, LC3B, and p62 was examined by Western blot. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. * p < 0.05 vs. untreated group; # p < 0.05 vs. only-TSA group. TSA, trichostatin A; CC, compound C.