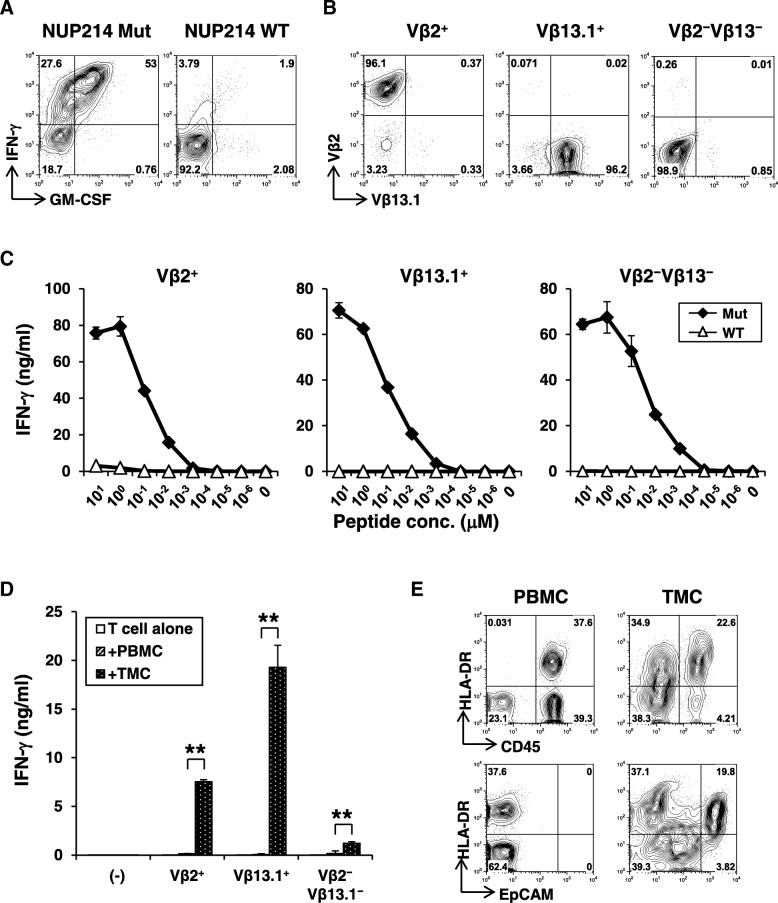
Fig. 4.
Characterization of NUP214 neoepitope-specific CD4+ T-cells. a Peptide reactivity of a NUP214 neoepitope-specific CD4+ T-cell line. IFN-γ and GM-CSF production on CD4+ T-cells against mutated or wild-type NUP214 peptide-pulsed autologous EBV-transformed B (EBV-B) cells were determined by intracellular cytokine staining. b Establishment of NUP214 neoepitope-specific CD4+ T-cell clones. TCR Vβ2+, Vβ13.1+, or Vβ2−Vβ13.1− cells in the NUP214 neoepitope-specific CD4+ T-cell lines were isolated. After expansion, each T-cell clone was stained by TCR Vβ subtype-specific antibodies. c Avidity of NUP214 neoepitope-specific T-cell clones. Vβ2+, Vβ13.1+, and Vβ2−Vβ13.1− CD4+ T-cell clones (50,000 cells) were stimulated with autologous EBV-B cells (25,000 cells) pulsed with NUP214 mutated or wild-type peptide in a 96-well round bottom plate for 24 h. IFN-γ level in the culture supernatant was measured by ELISA. The data represents mean ± s.d. of duplicate wells. d Reactivity of Vβ2+, Vβ13.1+, and Vβ2−Vβ13.1− T-cell clones against autologous tumor cells. PBMCs or TMCs (100,000 cells) were co-cultured with Vβ2+, Vβ13.1+, or Vβ2−Vβ13.1− NUP214 neoepitope-specific CD4+ T-cells (50,000 cells) or without T-cells (−) for 24 h. TMCs: tumor tissue-derived mononuclear cells. IFN-γ production was measured by ELISA. The data represent mean + s.d. of triplicate wells. **p < 0.01 (student’s t-test) compared to IFN-γ level against PBMCs. e Expression of MHC class II on CD45+ immune cells and EpCAM+ tumor cells. HLA-DR expression on CD45+ or EpCAM+ cells from PBMCs or TMCs were analyzed by flow cytometry