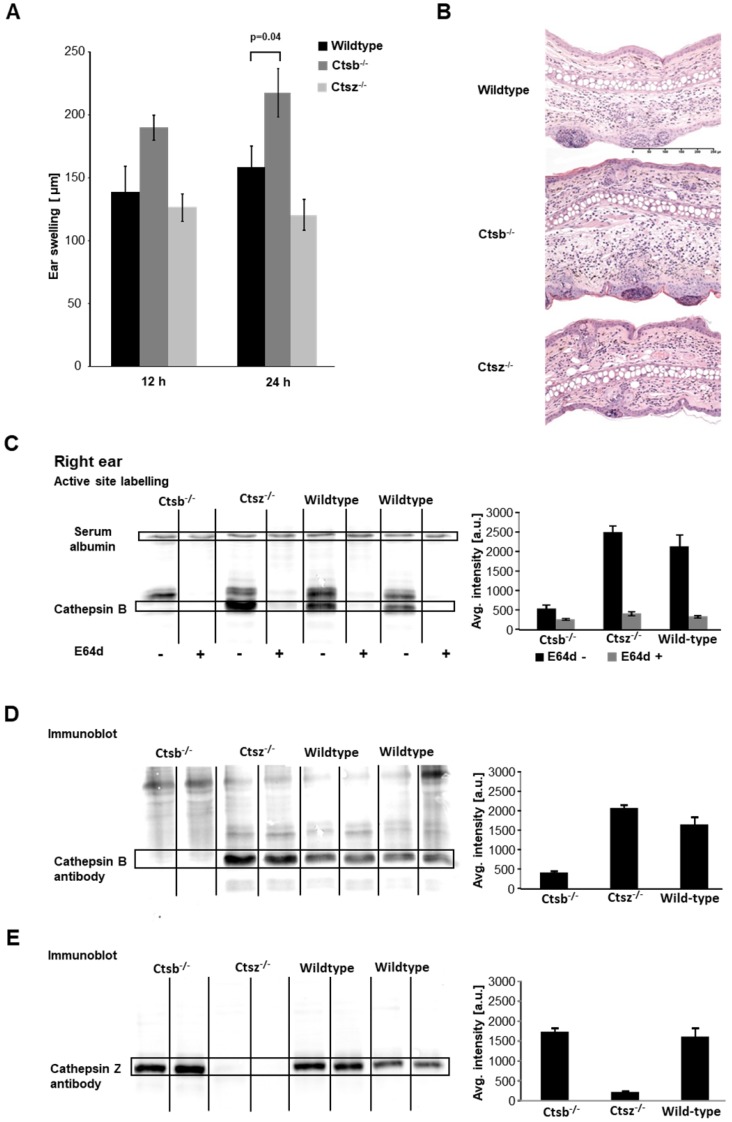
Figure 5.
Effect of cathepsin B deficiency. Ctsb-/- mice, Ctsz-/- mice and wild-type mice were sensitized on the abdomen with 5% TNCB and challenged seven days later on the right ear. A: We observed significantly enhanced ear swelling in Ctsb-/- mice during acute cutaneous DTHR 24 h after challenge compared to that in wild-type mice, while Ctsz-/- mice showed a trend towards reduced ear swelling compared to that in wild-type mice (wild-type: n=8; Ctsb-/- mice: n=11; Ctsz-/- mice: n=3; two-tailed Student's t-test with Bonferroni correction p< 0.025; mean±SEM). B: H&E staining of inflamed ear tissue harvested 24 h after TNCB challenge revealed more severe ear swelling, more pronounced edema and a higher density of infiltrating neutrophils in Ctsb-/- mice than in wild-type mice. However, Ctsz-/- and wild-type mice exhibited no histopathological differences. C: Active site labeling revealed a diminished cathepsin B-sized band in the lanes corresponding to samples from Ctsb-/- mice. The cathepsin B bands in the lanes corresponding to samples from Ctsb-/- mice were more prominent than those in the lanes corresponding to samples from wild-type mice, suggesting upregulation of cathepsin B expression (Ctsb-/-: n=4; Ctsz-/-: n=3; wild-type: n=4). D: To confirm the identity of the bands detected by active site labeling, we performed immunoblotting on the same gel using a cathepsin B-specific antibody. Immunoblotting indicated a trend towards enhanced cathepsin B expression in Ctsz-/- mice and verified diminished cathepsin B expression in Ctsb-/- mice (Ctsb-/-: n=4; Ctsz-/-: n=3; wild-type: n=4). E: Immunoblotting using a cathepsin Z-specific antibody demonstrated a slight trend towards elevated cathepsin Z expression in some Ctsb-/- mice and virtually no cathepsin Z expression in Ctsz-/- mice (Ctsb-/-: n=4; Ctsz-/-: n=3; wild-type: n=4).