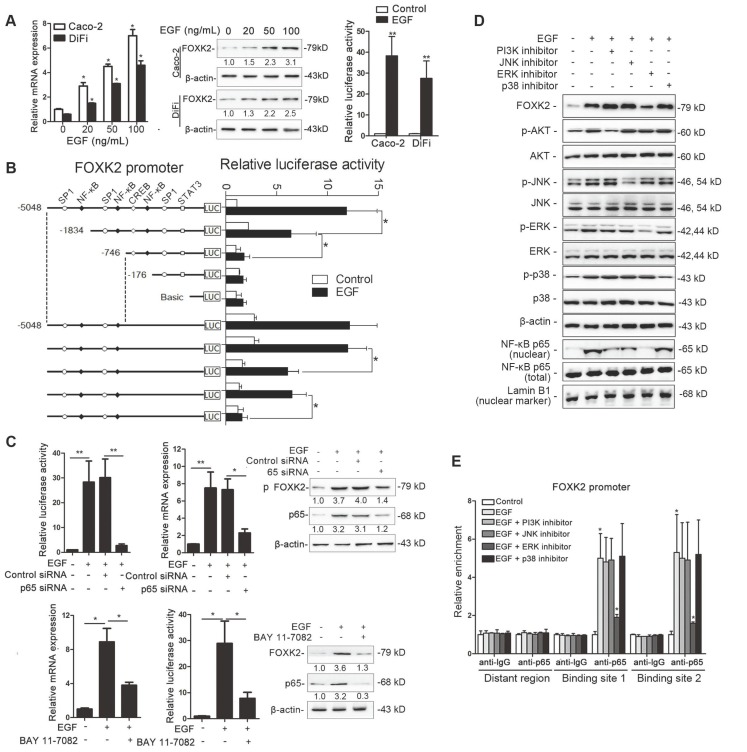
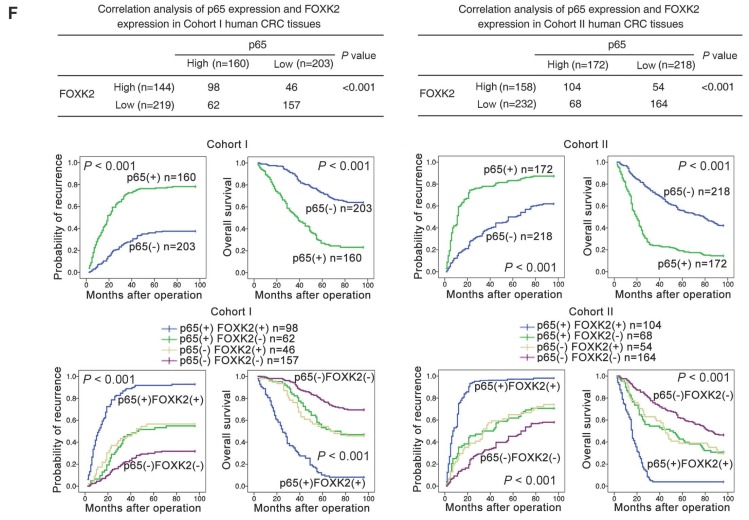
Figure 4.
EGF induces FOXK2 expression through the ERK/NF-κB pathway. (A) CRC cells were exposed to different EGF concentrations for 24 hours, followed by Western blotting and RT-qPCR to detect FOXK2 expression. Cells were incubated with or without EGF for 24 hours after transfection with the FOXK2 promoter luciferase reporter to determine luciferase activity. n = 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01 compared with the control. The data are presented as the mean±s.d. (B) Relative luciferase activity was determined after serially truncated and mutated FOXK2 promoter in Caco-2 cells incubated with EGF. * P < 0.05 compared with the control. The data are presented as the mean±s.d. (C) Caco-2 cells were transfected with a small-interfering RNA (siRNA) for p65 or control siRNA, vehicle or the NF-κB inhibitor BAY 11-7082, followed by EGF treatment for 24 hours. FOXK2 promoter activity and expression were measured via Western blotting, RT-qPCR and luciferase activity assays. n = 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01 compared with the control. The data are presented as the mean±s.d. (D) Caco-2 cells were treated with EGF and potent inhibitors of PI3K, JNK, ERK and p38. Western blotting was used to quantify the protein levels of FOXK2 as well as the total and phosphorylated levels of p38, JNK, ERK and AKT, as well as the levels of nuclear and total p65. β-actin and LaminB1 served as the loading control. n = 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. (E) ChIP assays demonstrated that EGF caused NF-κB to directly bind to the FOXK2 promoter through the ERK pathway. n = 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. * P < 0.05 compared with the control. The data are presented as the mean±s.d. (F) The correlation between p65 and FOXK2 expression in two independent cohorts of CRC patients (cohort I, n = 363; cohort II, n = 390). Kaplan-Meier analysis of the correlations of p65 expression, FOXK2 expression, and p65/FOXK2 coexpression with overall survival and recurrence in cohort I and cohort II. + High; - Low.