Figure 1.
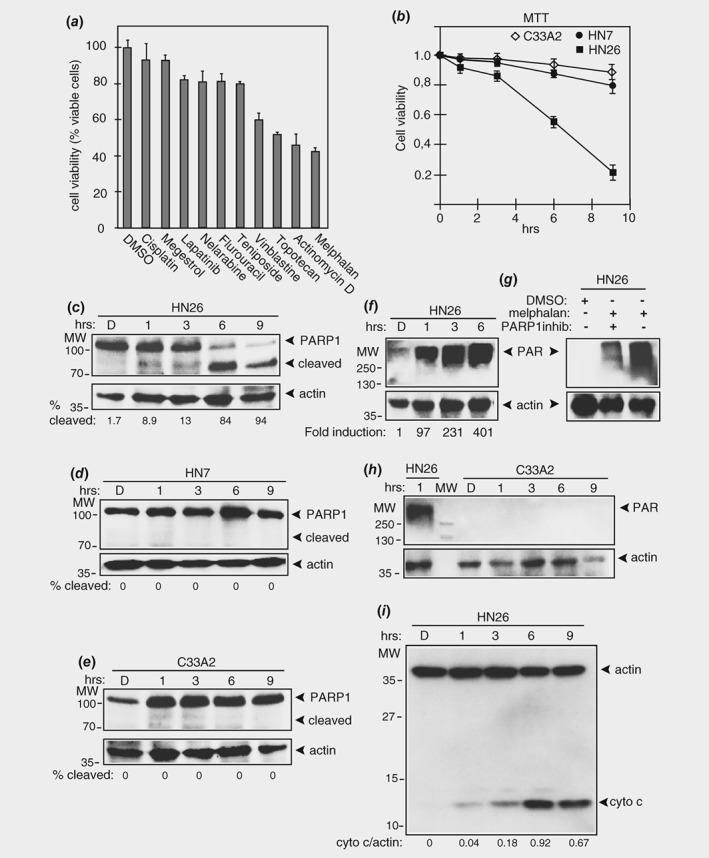
Melphalan reduces viability and induces apoptosis of HPV16 positive tonsillar cancer cells. (a) MTT assay on HN26 cells incubated for 24 h with 100 μM of the indicated cancer drugs or carrier substance DMSO. Mean values of triplicates are shown. (b) Viability of C33A2 cervical cancer cells, HN7 head and neck cancer cells or HN26 tonsillar cancer cells treated with DMSO or 100 μM melphalan for the indicated time periods was determined with an MTT assay as described in Materials and Methods and plotted against time in melphalan. (c–e) Western blots of full length and cleaved poly [ADP‐ribose] polymerase (PARP1) in extracts from HN26 cells, HN7 cells or1 C33A2 cells treated with 100 μM melphalan for the indicated time periods. Poly ADP‐ribosylation (parylation) was monitored by Western blotting with monospecific antibody to poly (ADP‐ribose) (PAR) in cell extracts from HN26 cells (f) or C33A2 cells (h) treated with 100 μM melphalan for the indicated time periods. (g) Western blotting with monospecific antibody to poly (ADP‐ribose) (PAR) in HN26 cells treated with 100 μM melphalan in the absence or presence of PARP1 inhibitor A‐966492. (i) Apoptosis‐mediated release of mitochondrial cytochrome c into the cytoplasmic space as a marker for apoptosis in HN26 cells treated with 100 μM melphalan for the indicated time points. Method is described in Supporting Information methods. Antibody is listed in Supporting Information Table T2. D, DMSO.
