Figure 3.
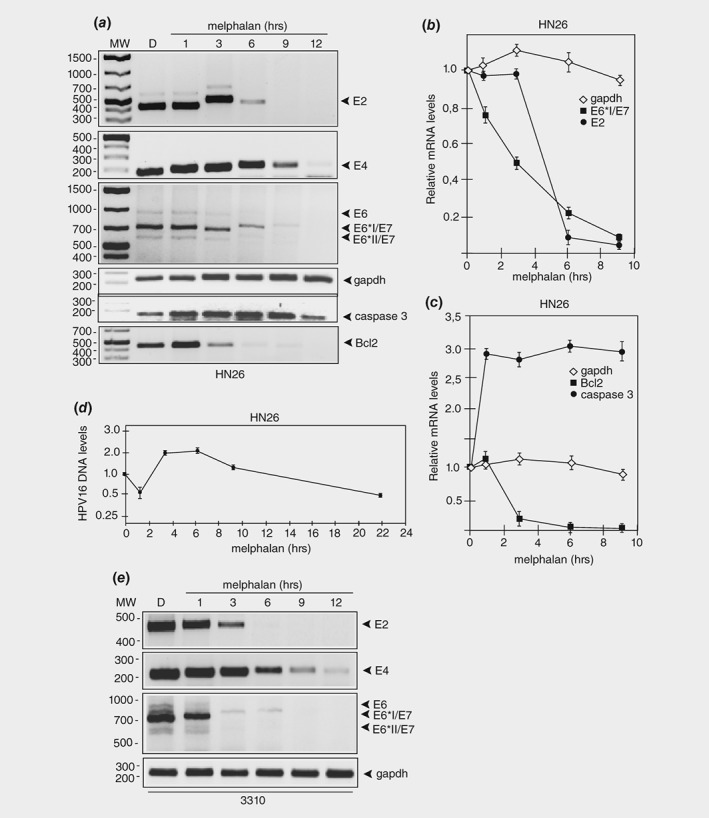
Melphalan causes rapid degradation of HPV16 E6 and E7 oncogene mRNAs in HPV16 positive tonsillar cancer cells. (a) RT‐PCR on total RNA extracted from HN26 cells treated with DMSO alone or 100 μM of melphalan for the indicated time periods. HPV16 E2, E4, E6, E6*I/E7 and E6*II/E7 mRNAs were monitored as well as spliced cellular gapdh, caspase 3 and Bcl2 mRNAs. (b, c) The RT‐PCR bands representing HPV16 mRNAs (b) or cellular mRNAs (c) were quantified and plotted against hours of melphalan treatment of the HN26 cells. (d) Quantitation of the HPV16 DNA genome with TaqMan PCR on Hirt DNA extracted at different time points from HN26 cells incubated in 100 μM melphalan. (e) RT‐PCR on total RNA extracted from HPV16‐immortalized human keratinocyte cell line 3,310 treated with DMSO alone or 100 μM of melphalan for the indicated time periods. HPV16 E2, E4, E6, E6*I/E7 and E6*II/E7 mRNAs were monitored as well as spliced cellular gapdh mRNAs. The location of the RT‐PCR primers in the HPV16 genome is shown in Supporting Information Figure 5B and the sequences of the RT‐PCR primers are listed in Supporting Information Table T1.
