Figure 4.
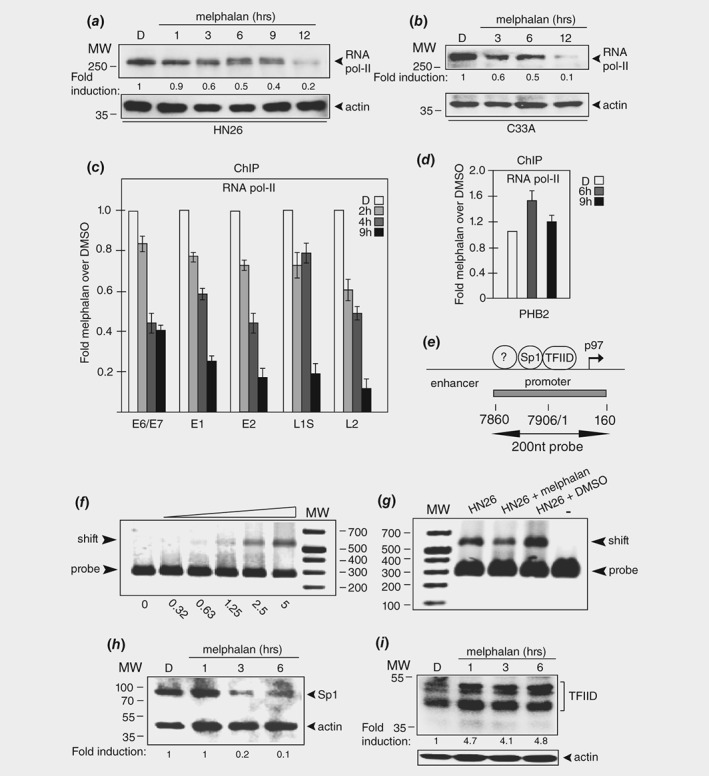
Melphalan inhibits transcription of the HPV16 E6 and E7 oncogenes. (a, b) Western blot with monospecific antibody to cellular RNA polymerase II in extracts from HN26 cells (a) or C33A2 cells (b) treated with DMSO or 100 μM melphalan for the indicated time points. (c) ChIP analyses on nucleosomes prepared from HN26 cells with monospecific antibody to RNA polymerase II and quantitative PCR (qPCR) of the indicated HPV16 amplicons. Hundred micromolar of melphalan was used. Primers are listed in Supporting Information Table T1. Mean values with standard deviations of the amount of immunoprecipitated DNA compared to input DNA are displayed. The q‐PCR values obtained for each primer pair with DNA extracted from DMSO‐treated HN26 cells were set to 1 to correct for differences between different ChIP extracts. Chip extracts were prepared from HN26 cells treated with melphalan for the indicated time‐periods. All samples were analyzed in two independent ChIP assays and all qPCR reactions were performed in triplicates. (d) ChIP analysis with monospecific antibody to RNA polymerase II of the cellular PHB2 gene. (e) Schematic representation of the enhancer/promoter at the HPV16 early promoter p97. The 200 nt dsDNA gel shift probe is indicated. Numbers refer to genomic positions in the HPV16R genome. (f) DNA‐protein gel‐shift assay with the HPV16 probe shown in Figure 7E and a two‐fold serial dilution of 5 μg of extract from HN26 cells. (g) DNA‐protein gel‐shift assay with the HPV16 probe shown in Figure 7E and extracts from untreated HN26 cells (HN26) or HN26 cells treated with DMSO or 100 μM melphalan. (h) Western blot on extracts from HN26 cells incubated with DMSO (D) or 100 μM melphalan for the indicated time‐periods with monospecific antibody to transcription factor Sp1 and actin. (i) Western blot on extracts from HN26 cells incubated with DMSO (D) or 100 μM melphalan for the indicated time‐periods with monospecific antibody to transcription factor TFIID and actin.
