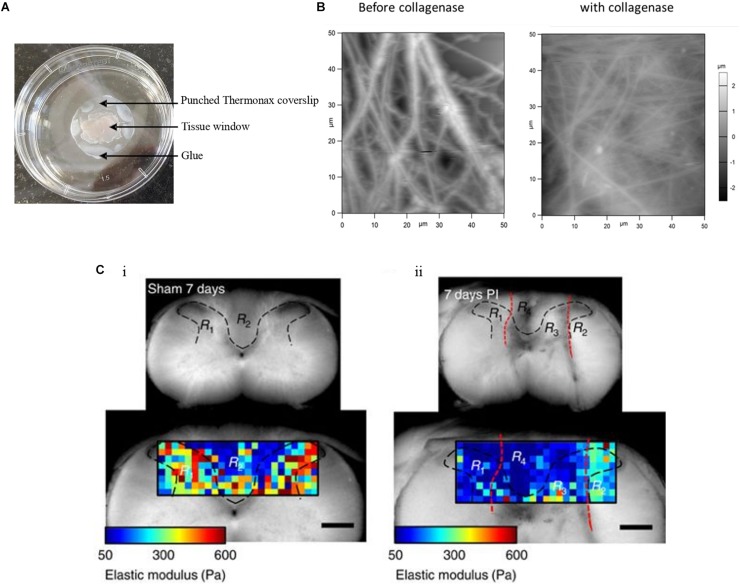
FIGURE 2.
Tissue sample immobilization and AFM imaging of mouse skin tissue sample. (A) Tissue samples are immobilized with punched Thermanox coverslips, glued to the Petri dish at their borders, thus avoiding direct contact of tissue with glue. AFM tip accesses the sample through the tissue window. (B) AFM height images show the presence of thick and rich ECM fibers in the mouse skin tissue matrix before addition of collagenase and after the addition of thick fibers, after which disappeared and decreased ECM fibers are seen (Joshi et al., 2017). (C) The gray (R1 and R3 in both i and ii) and white (R2 and R4 in both i and ii) matter are indicated within the area (black dashed lines) of the transverse spinal cord section of a sham control and of an animal with a dorsal column crush lesion at 7 days post-injury. The elastic moduli values are represented by means of a color map. In ii, the injured areas are identified by the red dashed lines (Reprinted with the permission from Moeendarbary et al., 2017 and this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. To view the copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).