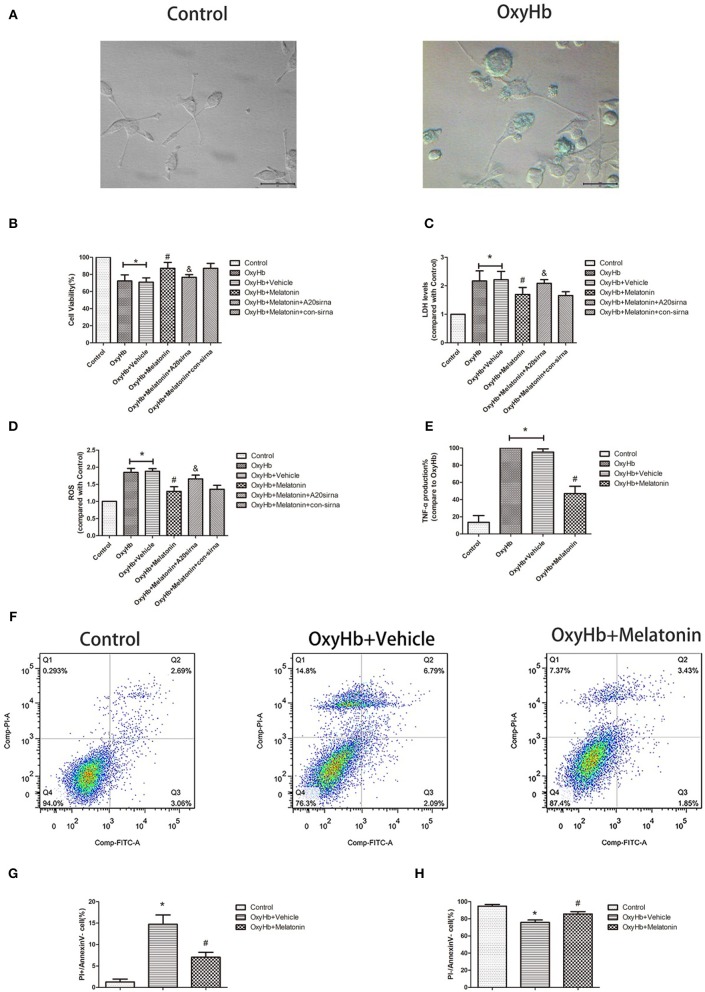
Figure 5.
OxyHb decreases cell viability, exerts cytotoxicity, and promotes inflammatory factor production in BV2 cells, thus inducing necroptosis in HT22 cells. Pre-incubation with melatonin effectively reduces the occurrence of these effects. (A) Representative photographs of BV2 cells in the control and OxyHb group (72 h). BV2 cells in the OxyHb group showed cell swelling and plasma membrane rupture. (B) Results of cell viability assay. (C) Result of LDH assay. (D) Results of ROS production assay. (E) Results of TNF production assay in BV2 cell supernatant. OxyHb increased TNF production in BV2 cells, whereas melatonin significantly suppressed this. (F–H) Flow-cytometric analysis of HT22 cells cocultured with BV2 cells exposed to different treatments. HT22 cells cocultured with BV2 cells treated with OxyHb showed a higher necroptotic population (defined as PI+/FITC−), whereas melatonin significantly reduced the necroptotic population. *P <0.05 vs. control group (n = 6/group), #P <0.05 vs. OxyHb+vehicle group (n = 6/group), &P <0.05 vs. OxyHb+melatonin+con-siRNA group.