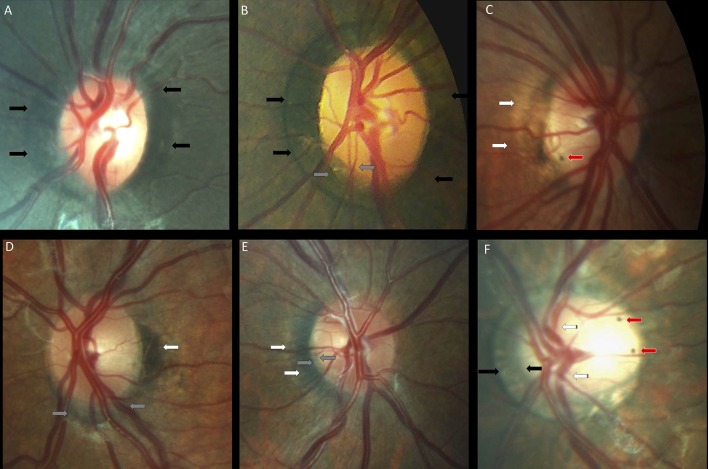
Figure 6.
Peripapillary pigmentary anomalies in children with Down syndrome. (A,B) Failure of the pigment epithelium to reach the optic disc margin for 360° of the optic disc margin in two children with Down syndrome (black arrows). (B) Inferotemporal small gray crescent (between the gray arrows). (C) Small intrapapillary pigment dot (red arrow) in an optic disc with temporal peripapillary atrophy (white arrows). (D) Choroidal crescent (gray arrows) below the disc with temporal pigment epithelium hypertrophy (white arrows). (E) Temporally-located conus pigmentosum (white arrows). The pigment extends into the optic disc substance, creating the appearance of a small gray crescent (gray arrows). (F) A tilted disc with an annular crescent (black arrows) and situs inversus of the vessels (striped arrows) in a child with Down syndrome and no refraction error. Two intrapapillary pigment dots are noted on the temporal side of the disc (red arrows).