Figure 4.
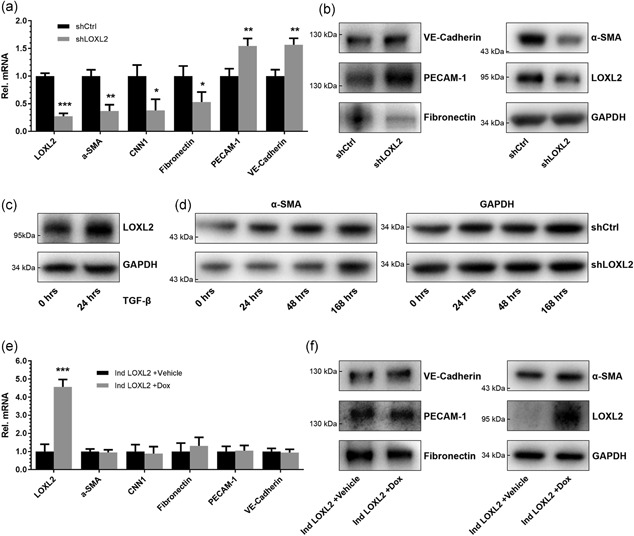
LOXL2 knockdown in EC reduces EndMT, but LOXL2 overexpression does not induce EndMT. (a) LOXL2 knockdown in EC reduces mRNA expression of mesenchymal markers α‐SMA, calponin 1, and fibronectin, and increases mRNA expression of endothelial markers PECAM‐1 and VE‐cadherin (n = 3, + SD, Student’s t test). (b) LOXL2 knockdown in EC increases protein expression of endothelial markers PECAM‐1 and VE‐cadherin, and reduces protein expression of mesenchymal markers α‐SMA and fibronectin. (c) The LOXL2 expression is increased in EC after stimulation with TGF‐β for 24 hr. (d) LOXL2 knockdown results in delayed TGF‐β‐mediated upregulation of α‐SMA in EC. (e) LOXL2 overexpression does not affect mRNA expression of mesenchymal markers α‐SMA, calponin 1, and fibronectin, or expression of endothelial markers PECAM‐1 and VE‐cadherin (n = 3, + SD, Student’s t test). (f) LOXL2 overexpression does not affect protein expression of endothelial markers PECAM‐1 and VE‐cadherin, or expression of mesenchymal markers α‐SMA and fibronectin; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001. EC: endothelial cells; EndMT: endothelial‐to‐mesenchymal transition; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; LOXL2: lysyl oxidase‐like 2; mRNA: messenger RNA; PBS: phosphate‐buffered saline; PECAM‐1: platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1; shCtrl: shRNA control; α‐SMA: α‐smooth muscle actin; shLOXL2: short hairpin‐mediated LOXL2 knockdown; TGF‐β: transforming growth factor‐β; VE‐cadherin: vascular endothelial cadherin
