Figure 10.
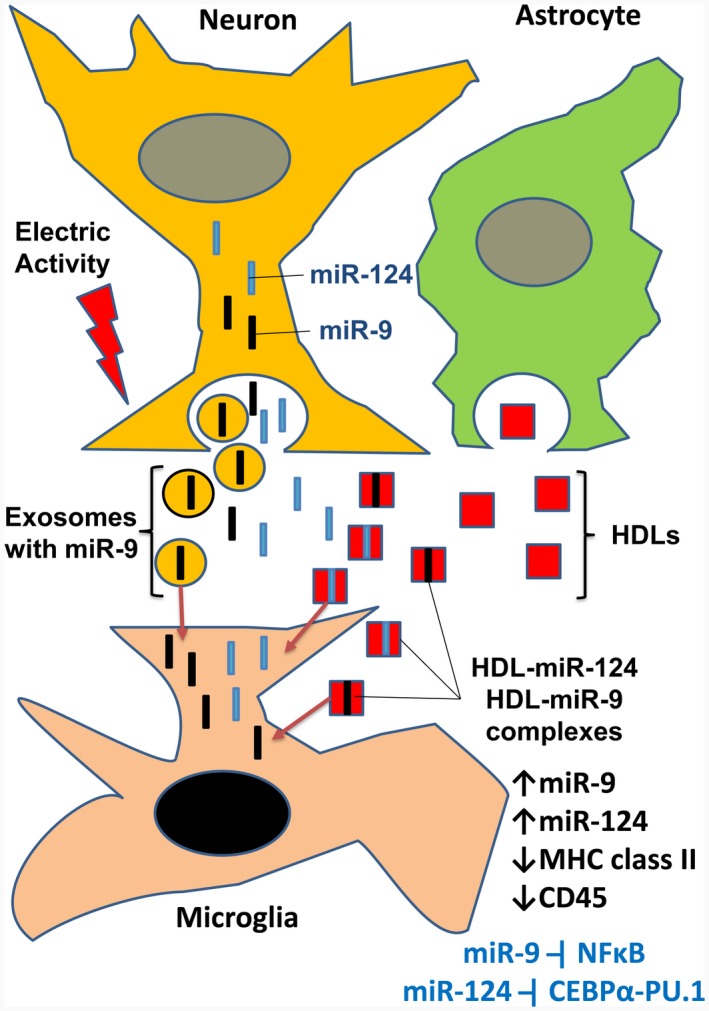
Model of horizontal transfer of miR‐124 and miR‐9 from neurons to microglia. Electrically active neurons secrete exosomes with miR‐9, as well as miR‐124 with miR‐9 in naked form and/or in complex with low molecular weight proteins. Astrocytes secrete HDLs that bind to miR‐124 and miR‐9 in the extracellular space. Exosomes with miR‐9, miR‐124:HDL, and miR‐9:HDL complexes are taken up by microglia. MiR‐9 and miR‐124 are translocated to the cytoplasm of microglia via fusion of miR‐9‐positive exosomes with plasma membrane or transport of HDL‐miR‐124 and HDL‐miR‐9 into the cytoplasm via scavenger receptors. In the cytoplasm, miR‐124 (and possibly miR‐9) deactivate microglia, leading to downregulation of MHC class II and CD45. Inside the cell, miR‐124 are known to inhibit the CEBPα‐PU.1 pathway, whereas miR‐9 inhibit NFκB. Both of these pathways are important for macrophage/microglia activation and expression of activation markers such as MHC class II and CD45
