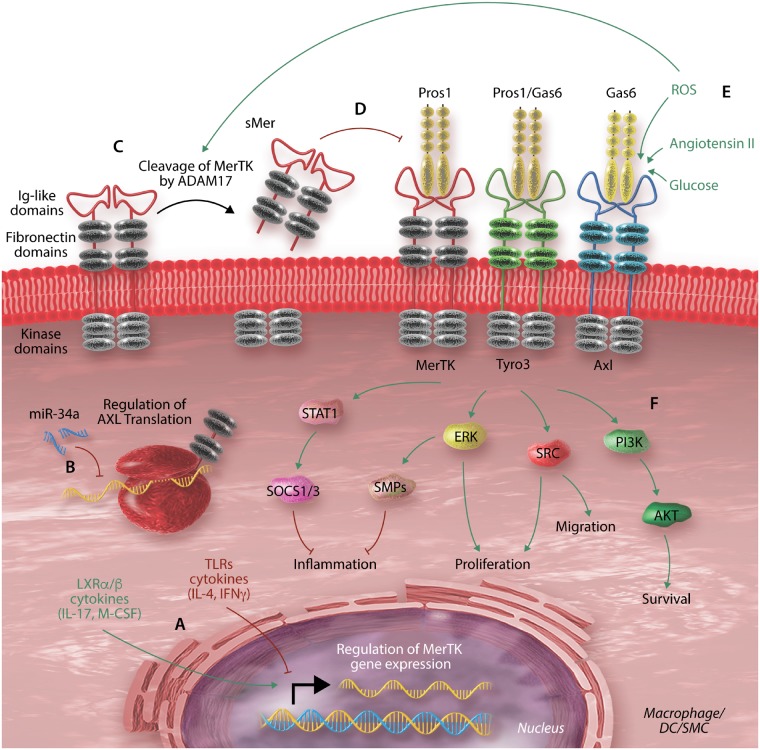
Figure 1.
Molecular regulation of the TAM receptors. The expression and activity of the TAM receptors is controlled by various factors at the transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and protein levels. (A) TAM receptor gene transcription can be up- or down-regulated by various factors, including cytokines. The figure shows mediators that specifically regulate MerTK transcription; the other TAM receptors are regulated by other mediators.43,44,46–48 (B) Post-transcriptional regulation by micro-RNAs such as miR-34a inhibition of Axl expression.50 (C) At the protein level, TAM receptors are rendered dysfunctional by cleavage of their extracellular domain by metalloprotease ADAM17.52,53 This process which can be driven by other environmental factors such as reactive oxygen species (ROS).53,55,56 (D) The soluble byproduct released may act as a decoy for the receptor ligands, thus inhibiting TAM receptor activity.57 (E) Activation of the receptors can also be enhanced by various environmental factors.58–60 (F) Activation of the TAM receptors subsequently induces various molecular pathways affecting cell function.16,60–62