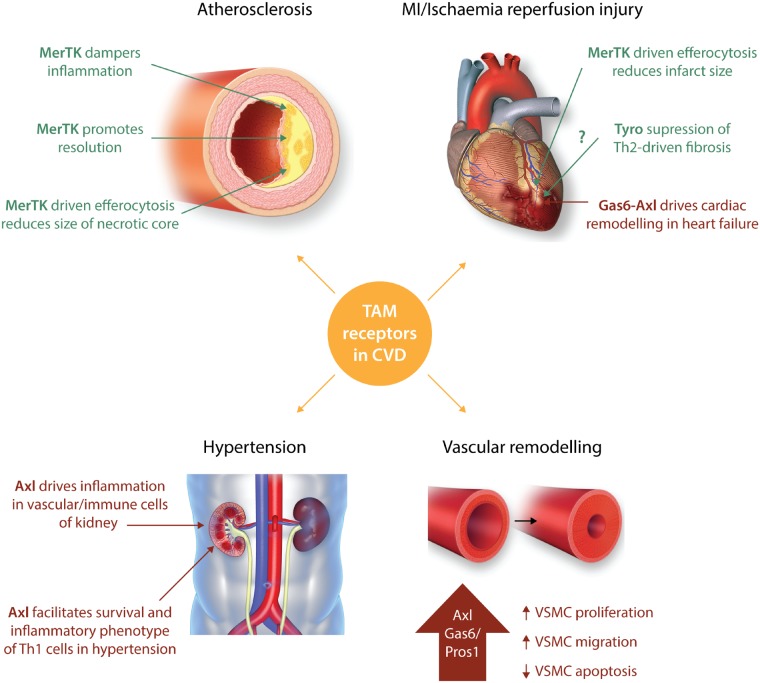
Figure 2.
Roles of TAM receptors in various cardiovascular diseases. Pathological roles for TAM receptor family members in cardiovascular disease are shown in red, with protective roles depicted in green. MerTK-deficiency has been shown to be detrimental in atherosclerosis models owing to its ability to dampen inflammation, promote resolution, and drive clearance of apoptotic bodies in the plaque necrotic core.30,32,56,130 These processes can be inhibited by MerTK cleavage, which occurs in necrotic, inflammatory plaques.31,55,56 In hypertension models, Axl expression in both vascular and immune cells has been implicated to drive pro-inflammatory responses in the kidney,67 and to affect T cell survival, vascular inflammation and remodelling.107 A major contribution to heart failure in coronary heart disease is due to tissue damage and fibrosis following myocardial infarction. Efficient clearing of dead cardiomyocytes is crucial for restoration of cardiac function, and MerTK has been shown to play a protective role in this setting.124 This process can be hindered by cleavage of MerTK, which is increased following ischaemia–reperfusion.56 Although Tyro3 could potentially have a protective effect on the myocardium, as it suppresses Th2 responses which drive cardiac fibrosis,136,140–142 a direct causal link has not been shown to date. Gas6-Axl driven activation of the ERK signalling cascade in cardiomyocytes is implemented in the pathological remodelling which occurs in heart failure patients.35,96,97 Numerous studies have highlighted Axl to also have a pathological role in vascular remodelling through increasing VSMC proliferation, migration, and immune activation, while also inhibiting VSMC apoptosis.64,65,69,79