Figure 3.
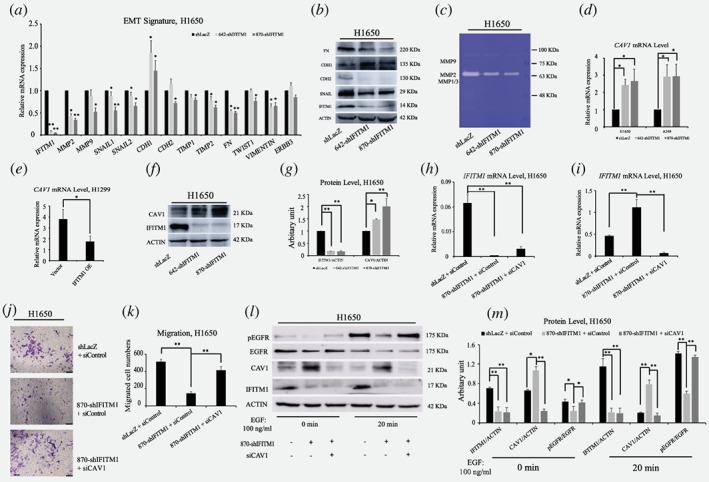
IFITM1 is essential for the maintenance of EMT signature of NSCLC cell lines in vitro. (a) Control (shLacZ) or IFITM1‐depleted (642‐shIFITM1 and 870‐shIFITM1) H1650 cells were treated with 5 ng/ml of TGF‐β, and the RNA levels of EMT genes were determined by RT‐qPCR. (b) Control (shLacZ) or IFITM1‐depleted (642‐shIFITM1 and 870‐shIFITM1) H1650 cell lysates were isolated and the protein level of EMT genes were probed with antibodies indicated. ACTIN was used as a loading control. (c) Supernatants obtained from control (shLacZ) or IFITM1‐depleted (642‐shIFITM1 and 870‐shIFITM1) H1650 cells were analyzed for enzymatic activity of MMP1/3, MMP2 and MMP9. (d‐g) NSCLC cell lines were transduced with either knocking down IFITM1 or overexpression of IFITM1, and the expression level of CAV1 was determined by RT‐qPCR (d and e) and immunoblot (f and g). ACTIN was used as a loading control. Representative images were shown (f) and quantification of protein levels was performed using Image J software from three separate experiments (g). (h‐m ) Control (shLacZ) or IFITM1‐depleted (870‐shIFITM1) H1650 cells were transiently transfected with either negative control (siNeg) or siCaveolin‐1 (siCAV1), and the expression of IFITM1 and CAV1 was determined by RT‐qPCR (h and i) and immunoblot (l and m). The transduced cells were either tested to determine migratory ability (j and k), or treated with 100 ng/ml of EGF to determine pEGFR level (l and m). Representative images were shown (l) and quantification of protein levels was performed using Image J software (m). The data are shown as mean ± SEM of three independent. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.001) [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
