Figure 2.
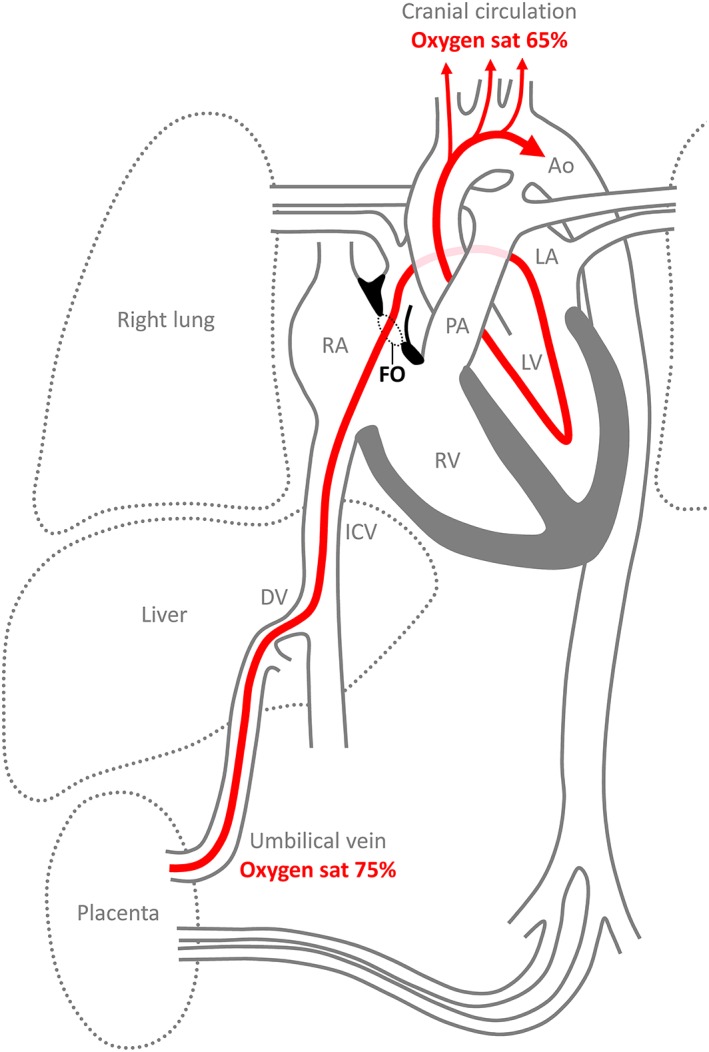
Overview of the fetal circulation, emphasizing the route of oxygen‐enriched blood (red) from the placenta, through the foramen ovale (FO), to the cranial circulation. This route entails two shunts, through the ductus venosus (DV) and the foramen ovale. The third fetal shunt is from the pulmonary artery (PA) through the ductus arteriosus to the aorta (Ao). The oxygen saturation (sat) only drops from ~75–65% from the placenta to the cranial arterial circulation. This suggests that the stream of oxygen‐enriched blood avoids mixing with much of the oxygen‐poor blood coming from the inferior caval vein (ICV) and other systemic veins. It also shows that a large proportion of the left ventricular output stems from the blood shunted across the foramen ovale, a flow that equals ~20% of cardiac output, with the remainder of the output stemming from the pulmonary veins. LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle.
