Figure 6.
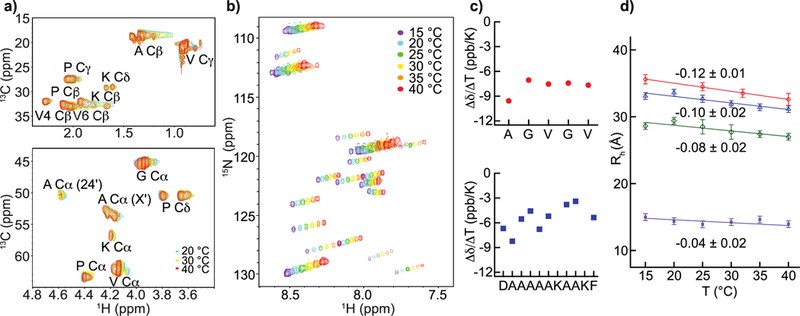
Temperature invariance of the disordered hydrophobic domains and temperature-driven compaction of designed elastins. (a) Superimposed 13C HSQC spectra of minielastin 4 obtained at 20 °C (green), 30 °C (yellow) and 40 °C (red). None of the resonances significantly changes chemical shift. (b) Superimposed 15N HSQC spectra of minielastin 4 obtained at 15–40 °C (c) Graphs of HN chemical shift temperature coefficients obtained from (b) for the residues in the hydrophobic module (red) and the cross-link module (blue) of minielastin 4. (d) Temperature dependent slopes of the hydrodynamic radii, Rh, of minielastins 1 (blue), 3 (green) and 4 (red) and module 24’ (purple) determined by NMR.
