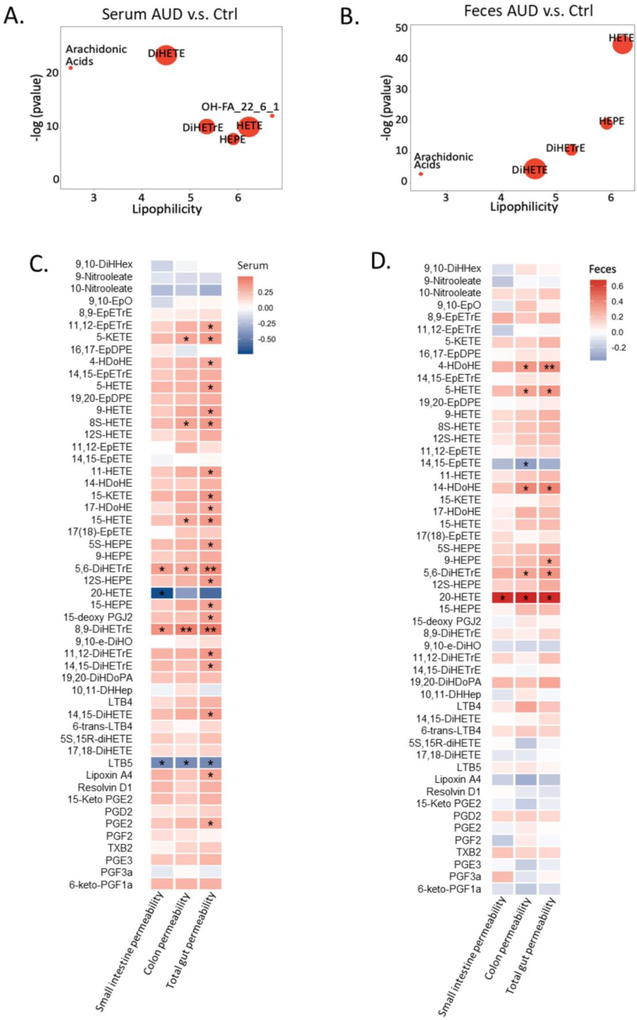
Figure 4.
ChemRICH analysis of serum oxylipins in alcoholic use disorder patients and controls (A). Ctrl: non-alcoholic control; AUD: alcohol use disorder; AH: alcoholic hepatitis. Significantly impacted metabolite clusters are shown in the plot (p < 0.05). The y-axis shows the most significantly altered clusters on the top. Red = increased in AUD patients. ChemRICH analysis of fecal oxylipins in alcoholic use disorder patients and controls (b). Ctrl nonalcoholic control; AUD alcohol use disorder; AH alcoholic hepatitis. Significantly impacted metabolite clusters are shown in the plot (p < 0.05). The y-axis shows the most significantly altered clusters on the top. Red=increased in AUD patients. Spearman correlation of serum oxylipins with intestinal permeability (C). Color intensity represents the correlation coefficient (R); Red: positive correlation; Blue: negative correlation. * p<0.05; ** p<0.01; *** p<0.001. Number of controls N=15; Number of AUD patients N=28. Spearman correlation of fecal oxylipins with intestinal permeability (D). Color intensity represents the correlation coefficient (R); Red: positive correlation; Blue: negative correlation. * p<0.05; ** p<0.01; *** p<0.001. Number of controls N=15; Number of AUD patients N=28.