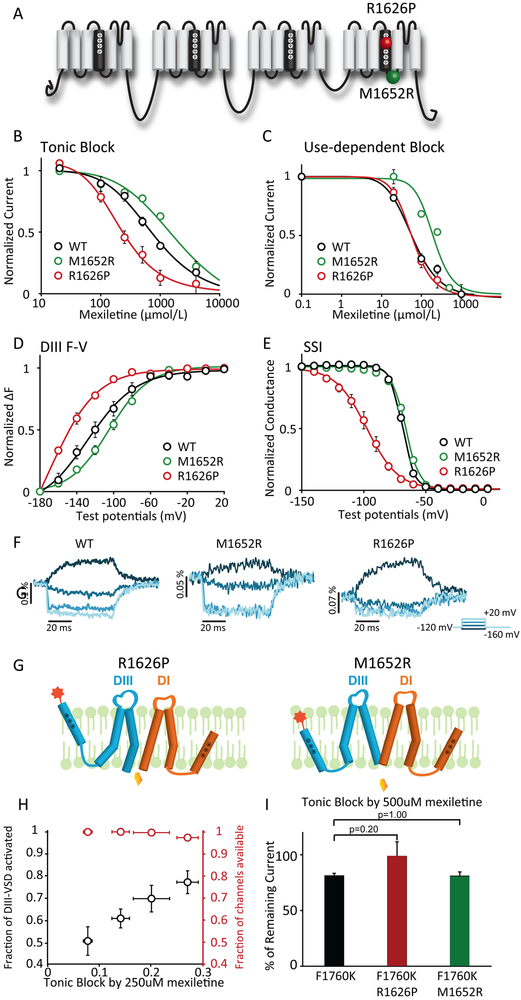
Figure 2: LQT variants with different sensitivities to mexiletine have distinct voltage dependence of DIII-VSD activation.
A. Topology of Nav1.5 channel and location of the two LQT mutations with distinct mexiletine sensitivity, R1626P (red ball, sensitive) and M1652R (green ball, insensitive).
B. Concentration dependence of tonic block (TB) by mexiletine for WT, R1626P, and M1652R channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes (n=3 tested for each drug condition). EC50 values were 761 μM for WT, 2035 μM for M1652R, and 211 μM for R1626P channels.
C. Concentration dependence of use-dependent block (UDB) by mexiletine (n=3 tested for each drug condition). Currents were normalized to the peak current elicited by the first depolarizing pulse. EC50 values were 58 μM for WT, 193 μM for M1652R, and 57 μM for R1626P channels.
D. Voltage dependence of steady-state fluorescence of DIII. The mean ± SEM is reported for groups of 3 to 4 cells. DIII F-V curve of M1652R showed depolarizing shift, while R1626P showed hyperpolarizing shift compared to WT channels.
E. Steady-state inactivation (SSI) curves of WT, R1626P, and M1652R channels (n=3 tested for each variant).
F. Representative DIII fluorescence traces from WT-M1296C, M1652R-M1296C, and R1626P-M1296C. All three constructs exhibit distinct fluorescence kinetics and voltage-dependence.
G. Proposed schematic showing possible mechanisms underlying the difference in mexiletine sensitivities between R1626P and M1652R. The DIII-VSD in the upward position represents the activated conformation. The lower position represents the inactivated conformation. At resting potential, R1626P has more activated DIII-VSD, which is coupled to the DIII pore domain (S5, S6), causing the pore to remain in a conformation with increase accessibility for mexiletine. In contrast, insensitive M1652R fewer activated DIII-VSDs, causing the DIII-pore to enter a conformation with less accessibility.
H. The relationships between % of block and the fraction of DIII-VSD activated, or the fraction of current available for four different holding potentials (−120, −110, −100, −90 mV) (n=3 tested for each holding potential). The fraction of current availability for four potentials are not significantly different from each other. The fraction of the DIII-VSD activated shows a linear relationship with the % of TB.
I. TB by 500 μM mexiletine for F1760K, R1626P F1760K, M1652R F1760K channels (n=4 tested for each variant). TBs are not significantly different examined with Mann-Whitney U test, suggesting that the F1760K eliminates LQT variant-dependent mexiletine sensitivity.