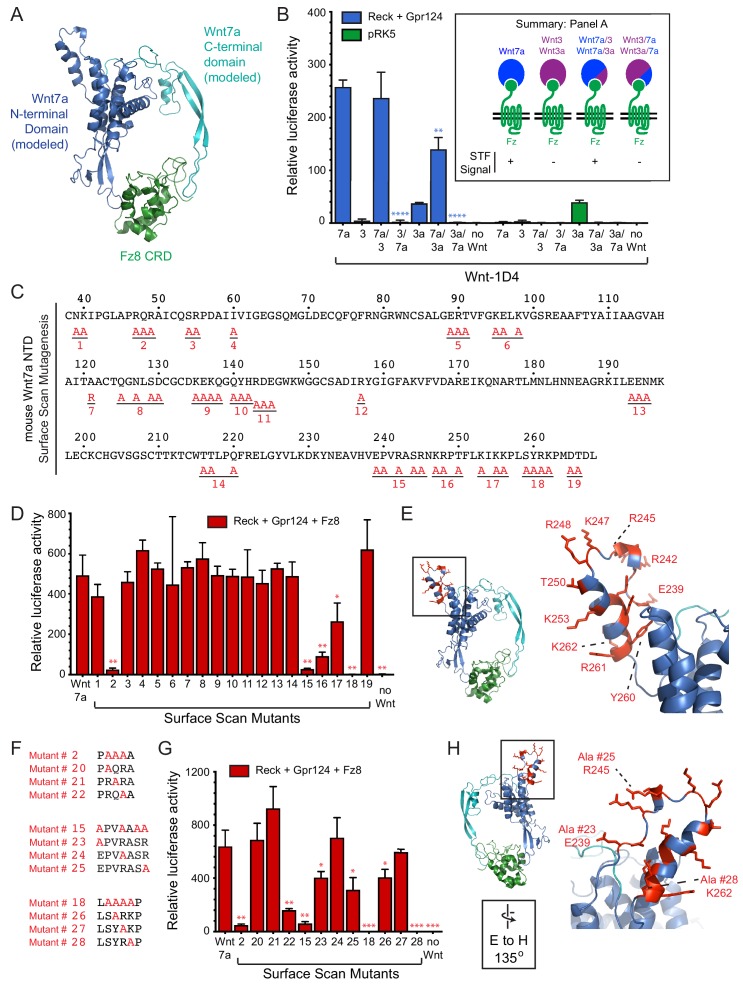
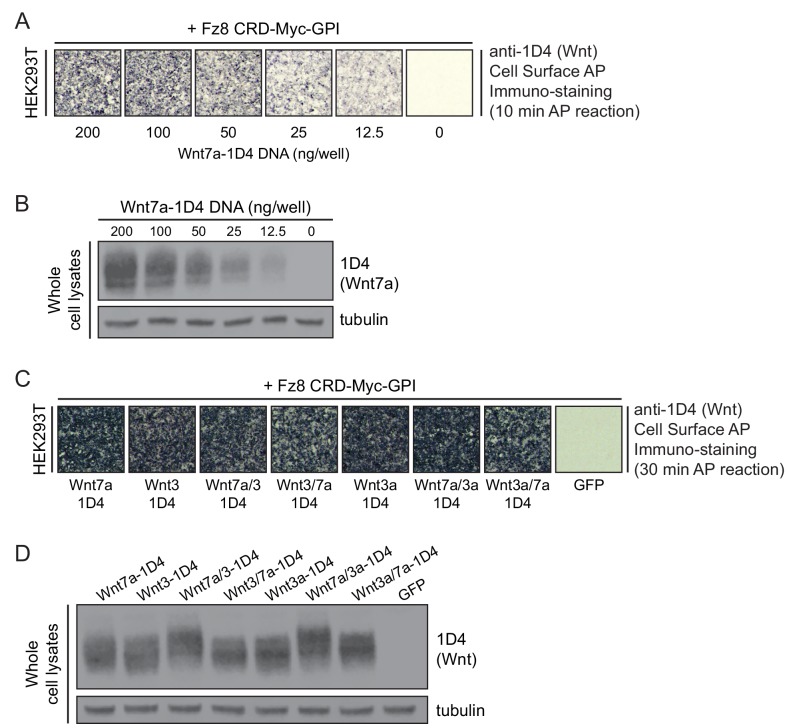
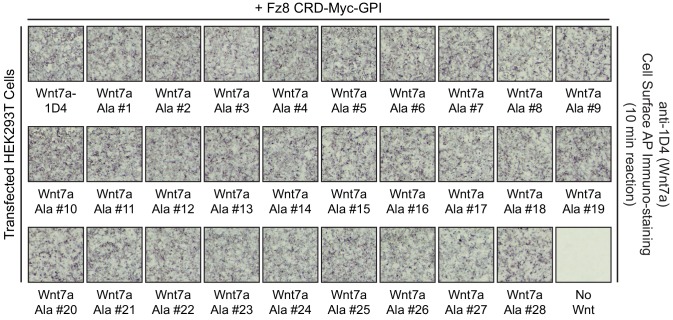
Figure 2. Wnt7a regions that are required for Reck/Gpr124-stimulated signaling.
(A) Backbone model of Wnt7a (N-terminal domain, blue; C-terminal domain, cyan) bound to Fz8 CRD (green) based on the Wnt-CRD crystal structure of Janda et al. (2012). The N-terminal domain of Wnt7a consists of ~270 amino acids (some of which were not resolved in the crystal structure), and the C-terminal domain consists of ~80 amino acids. (B) Beta-catenin signaling assay using STF cells transfected with Reck and Gpr124 (left) or pRK5 vector control (right), together with the indicated Wnts. Inset: summary of STF signaling. Statistical comparisons in (B), (D), and (G) are to WT Wnt7a. (C) Amino acid sequence of the N-terminal domain of mouse Wnt7a, with alanine scanning mutants indicated. (D) Beta-catenin signaling assay using STF cells transfected with Reck, Gpr124, and Fz8, together with WT or mutant Wnt7a. (E) Left, backbone model of Wnt7a bound to Fz8 CRD as in (A), with amino acids that are critical for Wnt7a signaling shown in red. Right, the boxed region is displayed at higher magnification. (F) Single alanine substitution mutants of Wnt7a, indicated in red. (G) Beta-catenin signaling assay as in (D) with WT or the indicated Wnt7a mutants. (H) Left, backbone model of Wnt7a bound to Fz8 CRD as in (A) except rotated 135 degrees, with amino acids that are critical for Wnt7a signaling shown in red. Right, the boxed region is displayed at higher magnification.