Fig. 5. Three photon excited fluorescence microscopy enables much deeper imaging than two photon excited fluorescence in mouse spinal cord.
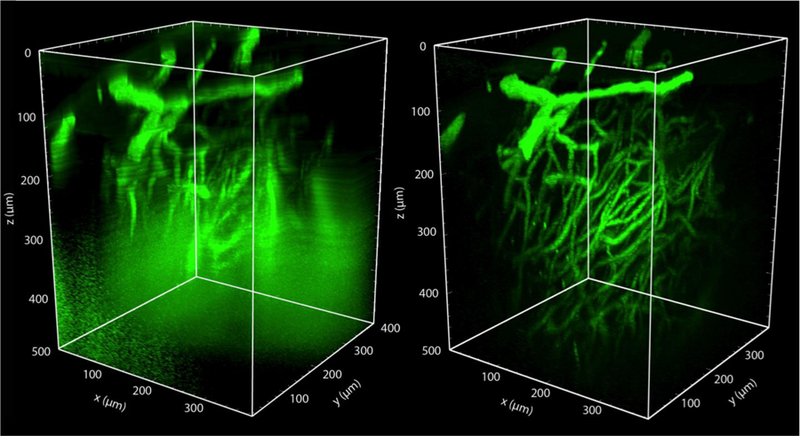
(left) Rendered 2PEF image stack of the spinal cord vasculature from a live, anesthetized mouse, labeled with an intravenous injection of 5% FITC-dextran. Image was taken with 800-nm excitation light (Chameleon, Coherent). (right) 3PEF imaging of the same region using 1,320-nm excitation light (Opera-F, Coherent). Out of plane fluorescence excitation leads to an increasing background with depth using 2PEF, ultimately limiting the imaging depth. This background is suppressed with 3PEF imaging, enabling visualization of individual capillaries as deep as 500 µm into the spinal cord (unpublished data).
